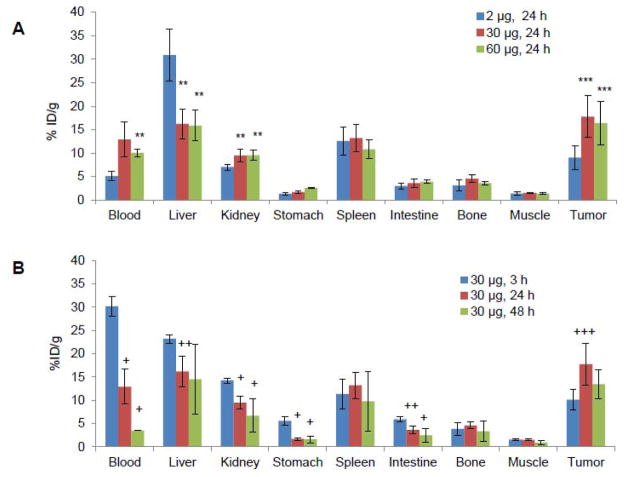
Figure 1.
Effects of total injection dose of amatuximab on the biodistribution of 64Cu-NOTA-amatuximab in nude mice with tumor size ~200 mm3 (range, 80~300 mm3). (A) The bidodistribution data from 64Cu-NOTA-amatuximab with different injection doses (10 μCi/2 μg, 10 μCi/30 μg, and 10 μCi/60 μg) are compared at 24 h p.i. in different organs, demonstrating that tumor uptake significantly increased and the liver uptake decreased when the injection dose was above 30 μg. (B) The biodistribution of 64Cu-NOTA-amatuximab at different post-injection times. The maximum tumor uptake of 64Cu-NOTA-amatuximab (10 μCi) was shown at 24 h post-injection when coinjected with 30 μg amatuximab. The data are mean ± S.D. (n = 5). Analysis of statistical significance in each organ uptake data (A) compared to the data from 2 μg injection and (B) compared to the data from 3 h p.i.: *P<0.001, **0.001<P<0.01, ***0.01<P<0.05; +P<0.001, ++0.001<P<0.01, +++0.01<P<0.05. Column, mean; bar, S.D.