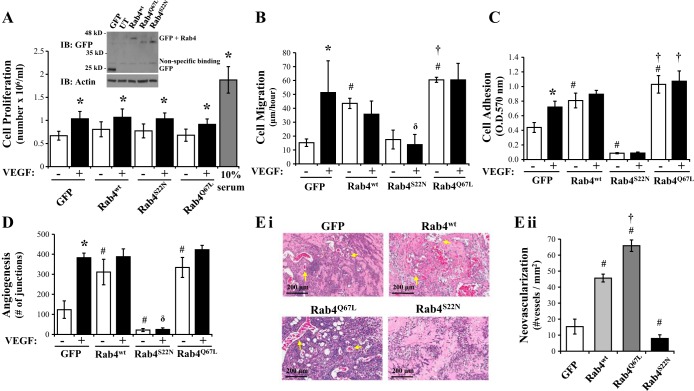
Fig. 4.
Rab4 activity regulates the angiogenic process in LMVEC. Equivalent numbers of LMVEC were transiently transfected with GFP, Rab4WT, Rab4Q67L, or Rab4S22N cDNA. A: following 24 h, cells were counted (as Fig. 1A) and lysates were assessed for Rab4 overexpression by Western blot analysis (inset). A representative blot is shown. B: following 48 h, cell migration was measured by wound-healing assay in the presence and absence of VEGF and migration (μm) of cells per hour was assessed (as Fig. 1B). C: following 48 h, cell adhesion to gelatin was measured by MTT assay (O.D.570nm) (as Fig. 1C). D: transfected cells were plated directly onto Matrigel-coated wells for 48 h. Cells were then treated with VEGF (50 ng/ml) for a further 6 h, and in vitro vessel formation, expressed as number of junctions formed, was assessed by using Angiogenesis Analyzer in ImageJ (as Fig. 2A). E: de novo vessel formation of transfected LMVEC was examined by using in vivo Matrigel plugs. Neovasculogenesis was determined by examining presence of blood vessels containing red blood cells within the Matrigel (as Fig. 2B). Images were captured using Aperio ScanScope CS (Ei) and number of vessels was quantified (Eii). Images were captured at ×10 magnification, scale bar 200 μm. Arrows demonstrate examples of neovasculogenesis within plugs as determined by presence of red blood cells within vessels. Data are presented as means ± SD; n = 4 (A), n = 3–5 (B), n = 5–6 (C), n = 4 (D), n = 5 (E); *P < 0.05 vs. vehicle, #P < 0.05 vs. GFP, δP < 0.05 vs. VEGF, †P < 0.05 vs. Rab4wt.