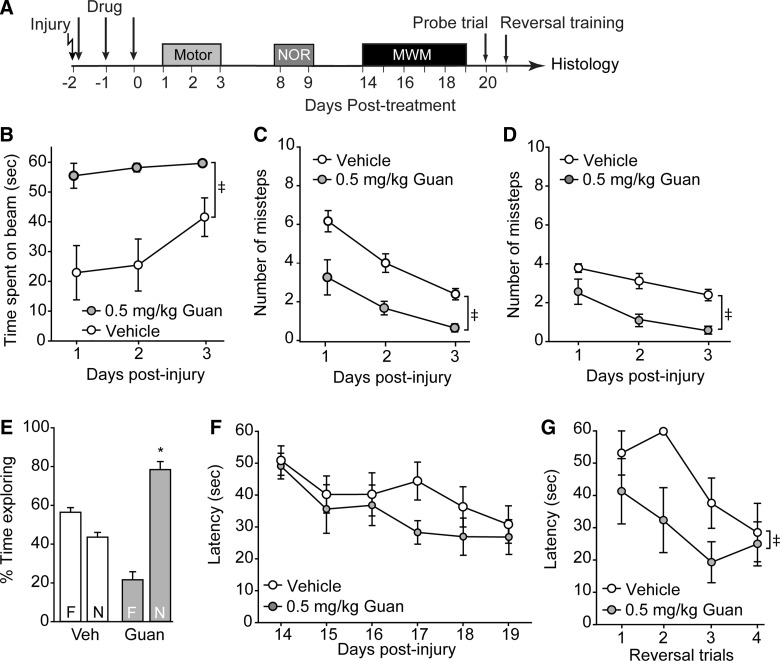
FIG. 4.
Low-dose guanabenz improves outcome after traumatic brain injury. (A) Controlled cortical impact animals were treated starting 30 min postinjury with either 0.5 mg/kg of guanabenz or vehicle (n=6/group), then tested for their motor and cognitive abilities. Rats treated with low-dose guanabenz had improved performance in the (B) beam balance task and displayed fewer (C) contra- and (D) ipsilateral foot faults than vehicle-treated injured animals. (E) Recognition memory, but not (F) spatial learning, was improved as a result of low-dose guanabenz treatment. (G) Reversal learning was significantly improved in injured rats treated with 0.5 mg/kg of guanabenz. Please note that the vehicle-treated group is the same as that shown in Figure 3. Data are presented as the mean±standard error of the mean. ‡Significant difference by two-way repeated measures analysis of variance. *p<0.05. NOR, novel object recognition; MWM, Morris water maze; Veh, vehicle; Guan, Guanabenz.