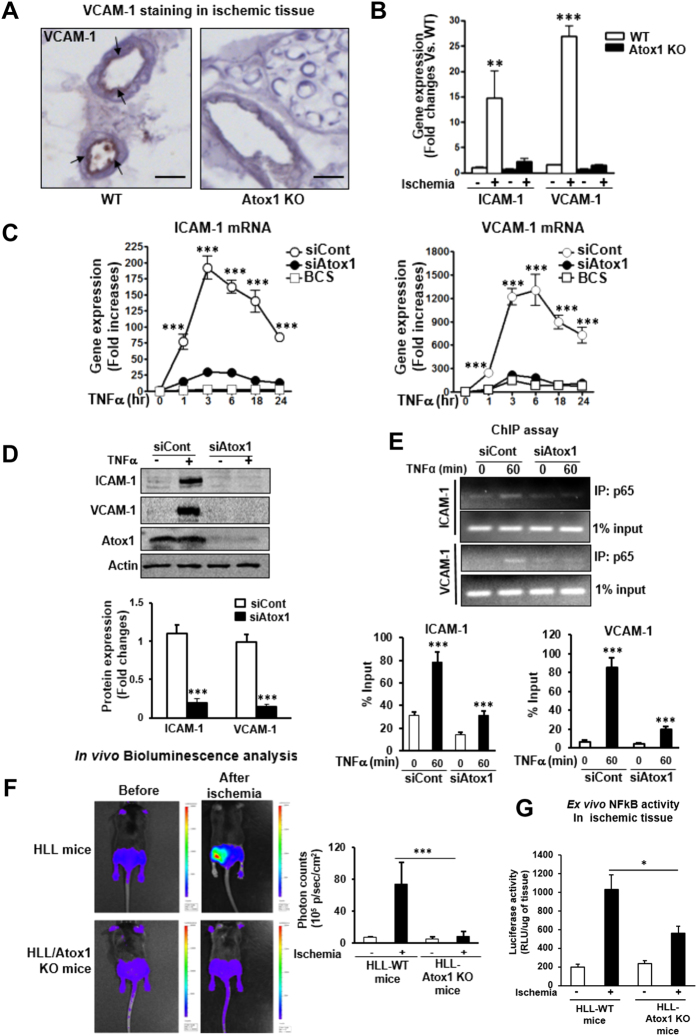
Figure 5. Atox1 is required for adhesion molecules expression in a Cu-dependent manner via activating NFκB in inflamed ECs.
(A) Representative images for VCAM-1 staining in ischemic adductor muscles in WT and Atox1 KO mice at day 1 (n = 4). Scale bars = 100μm. (B) Expression of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 mRNAs in ischemic and non-ischemic muscles at day 3 (n = 4). (C) HUVECs transfected with Atox1 or control siRNAs, or treated with BCS were stimulated with TNFα (10ng/ml), and ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 mRNAs were measured (n = 12). (D) HUVECs transfected with Atox1 or control siRNAs were incubated with TNFα for 18 hours, and VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 protein expression was measured. Actin was loading control (n = 8). (E) ChIP assay showing a role of Atox1 in TNFα-induced p65 NFkB binding to the ICAM-1/VCAM-1 promoter in vivo. HUVECs transfected with Atox1 or control siRNAs stimulated with TNFα were precipitated with the anti-p65NFkB antibody. The ICAM-1/VCAM-1 promoter region was amplified by PCR. Input of nuclear DNA was used as PCR control. (n = 4). (F) In vivo bioluminescence imaging of NFkB reporter mice (HLL mice) and HLL mice crossed with Atox1 KO mice before and after hindlimb ischemia at day 3. (n = 3). Representative images (left) and quantification of bioluminescence intensity (right). (G) Luciferase activity in homogenates of non-ischemic and ischemic gastrocunemious tissue from HLL and HLL/Atox1 KO mice at day 3 (n = 5). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001