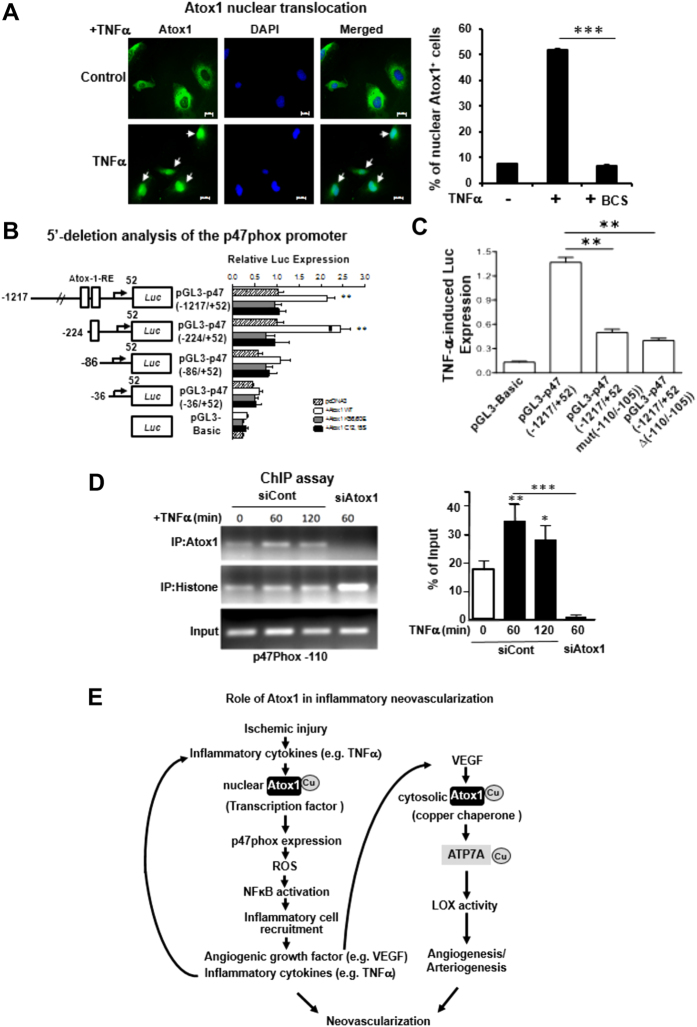
Figure 8. Atox1 promotes p47phox transcription by binding to its promoter in ECs activated by TNFα in a Cu-dependent manner.
(A) Immunofluorescence staining of Atox1. HUVECs stimulated with TNFα (10 ng/ml) pretreated with or without Cu chelator BCS were immunostained for Atox1 or nuclear marker DAPI. Percentage of Atox1 + cells in nucleus was shown in right (n = 3). (B) Identification of Atox1 responsive elements (Atox1-RE) in a p47phox promoter. HEK293 cells were transiently transfected with indicated promoter luciferase constructs along with pcDNA/Atox1-WT or mutants Atox1 mutated at nuclear translocation signal (K56,60E) or Cu-binding domains (C12,15S). Two days after transfection, the luciferase activity was measured (n = 3). (C) HUVECs were transfected with a p47phox promoter luciferase reporter construct (pGL3-p47phox promoter (−1217/+52)) with or without mutation or deletion of the Atox1-RE (−110 to −105 region) (n = 3). (D) ChIP assay showing Atox1 binding to the p47phox promoter in vivo. HUVECs transfected with Atox1 or control siRNAs were treated with TNFα (10ng/ml). After precipitation with anti-Atox1 antibody, the p47phox promoter region (the Atox1-RE (−110 to −105 region)) was amplified by PCR (n = 4). Input nuclear DNA was used as PCR control. *p < 0.05. #p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. (E) Models for role of Atox1 in inflammatory neovascularization, which is dependent on arteriogenesis/angiogenesis and inflammation. Atox1 functions as a Cu chaperone mediated through ATP7A to increase LOX activity involved in VEGF-induced angiogenesis as well as a Cu-dependent transcription factor for NADPH oxidase organizer p47phox to increase the ROS-NFkB-VCAM-1/ICAM-1 axis in ECs inflamed with TNFα. This in turn promotes recruitment of inflammatory cells which secrete TNFα and VEGF. This represents a novel positive feedback loops whereby Cu transport protein Atox1 promotes inflammatory neovascularization.