Figure 6.
Nr2f6 Suppresses Th1 CD4+ T Cell Activation
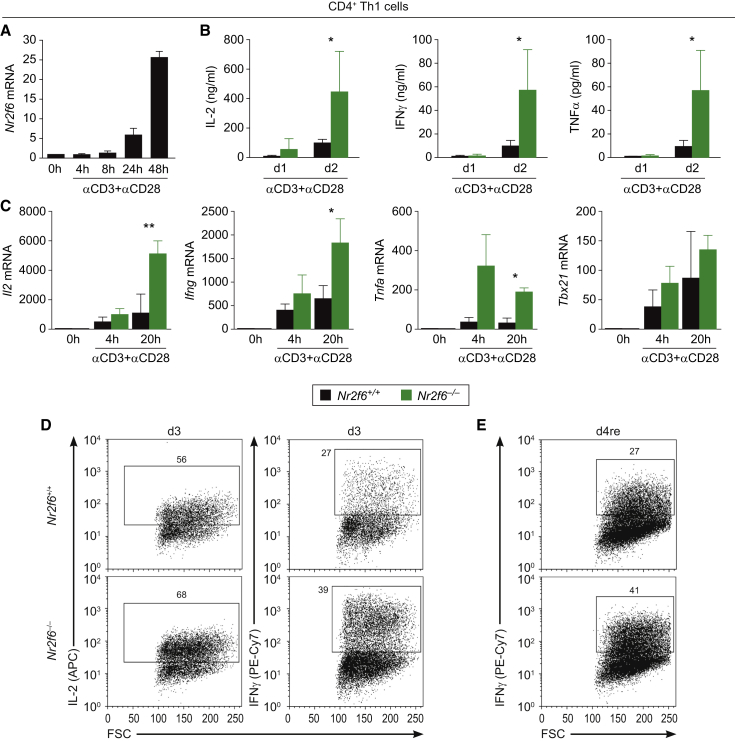
(A) In vitro qRT-PCR analysis of Nr2f6 mRNA in wild-type CD4+ T cells during Th1 differentiation activated with anti-CD3 mAb (5 μg) and anti-CD28 mAb (1 μg) at the indicated time points (n = 3).
(B) Bioplex technology was used to demonstrate significantly increased secretion of the pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-2 (p = 0.045), IFN-γ (p = 0.047), and TNF-α (p = 0.046) in the supernatant of in-vitro-activated Nr2f6−/− versus wild-type CD4+ T cells at day 1 and day 2 of differentiation under Th1-polarizing conditions (n = 3).
(C) In vitro qRT-PCR analysis similarly detected enhanced transcript expression levels of Il2 (p = 0.003), Ifng (p = 0.044), Tnfa (p = 0.017), but not Tbx21 (p = 0.17) mRNA in Nr2f6−/− CD4+ Th1 cells compared to Nr2f6+/+ cells upon activation with anti-CD3 (5 μg) and anti-CD28 (1 μg) at the indicated time points (n = 3). Expression was normalized to the housekeeping gene GAPDH and presented as fold induction of unstimulated cells. Summary graphs represent the mean ± SD, data are representative for at least two independent experiments, and statistical differences were evaluated by applying two-way ANOVA.
(D and E) (D) Analysis of IL-2 and IFN-γ producing CD4+ Th1 T Nr2f6+/+ or Nr2f6−/− cells by flow cytometry after 3 days (3d) of Th1 driving conditions and (E) followed by a restimulation with anti-CD3 (5 μg) overnight (d4/re). Numbers within outlined areas indicate the percentage of cytokine-expressing cells, and one out of three representative experiments is shown.