Figure 2.
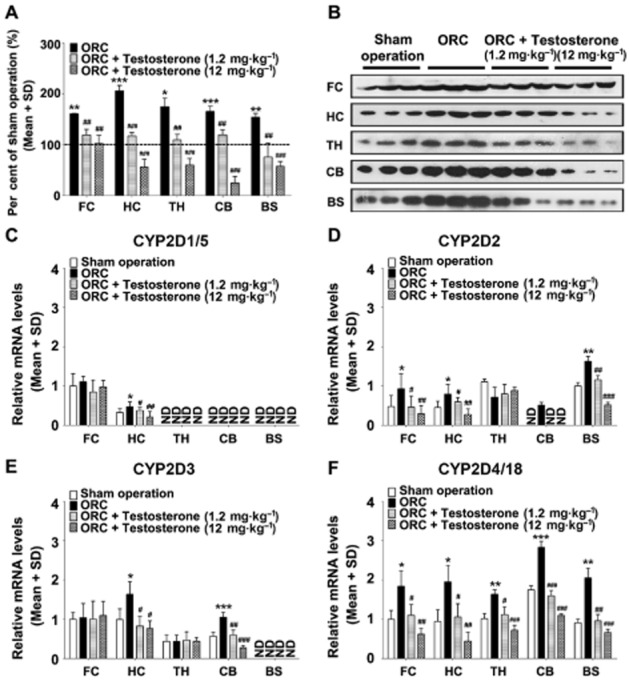
Testosterone supplementation attenuates the induction of CYP2D levels by orchiectomy. Compared with the sham operation group, CYP2D levels were significantly increased by orchiectomy in the frontal cortex, hippocampus, thalamus, cerebellum and brainstem (A). Brain CYP2D protein in orchiectomized rats decreased dose-dependently following testosterone supplementation. Compared with the sham operation group, orchiectomy markedly increased CYP2D4/18 mRNA levels in all brain regions tested (F), CYP2D2 mRNA levels in the frontal cortex, hippocampus, cerebellum and brainstem (D), CYP2D3 mRNA levels in the hippocampus and cerebellum (E) and CYP2D1/5 mRNA levels in the hippocampus (C). The induction of CYP2D mRNA levels by orchiectomy was decreased by testosterone supplementation. Representative immunoblots of the various brain regions are presented (B). ORC: orchiectomy. n = 3 per group, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001; significantly different from the sham operation group, #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001; significantly different from the orchiectomy group.
