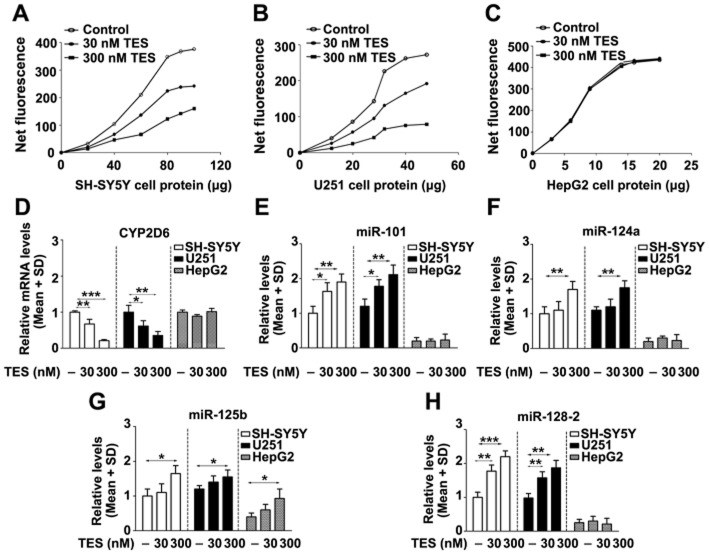
Figure 5.
Effects of testosterone on levels of CYP2D6 and miRNAs in SH-SY5Y, U251 and HepG2 cells. Testosterone decreased the level of CYP2D6 mRNA in SH-SY5Y and U251 cells, but not in HepG2 cells (D). The metabolism of AMMC increased with increasing amounts of cell proteins from SH-SY5Y (A), U251 (B) and HepG2 cells (C), whereas testosterone dose-dependently decreased AMMC metabolism in SH-SY5Y and U251 cells. Testosterone increased the levels of miR-101 (E), miR-124a (F) and miR-128-2 (H) in SH-SY5Y and U251 cells, but not in HepG2 cells. Testosterone in the higher concentration increased miR-125b (G) levels in SH-SY5Y, U251 and HepG2 cells. TES: testosterone. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001; significantly different from the respective controls.