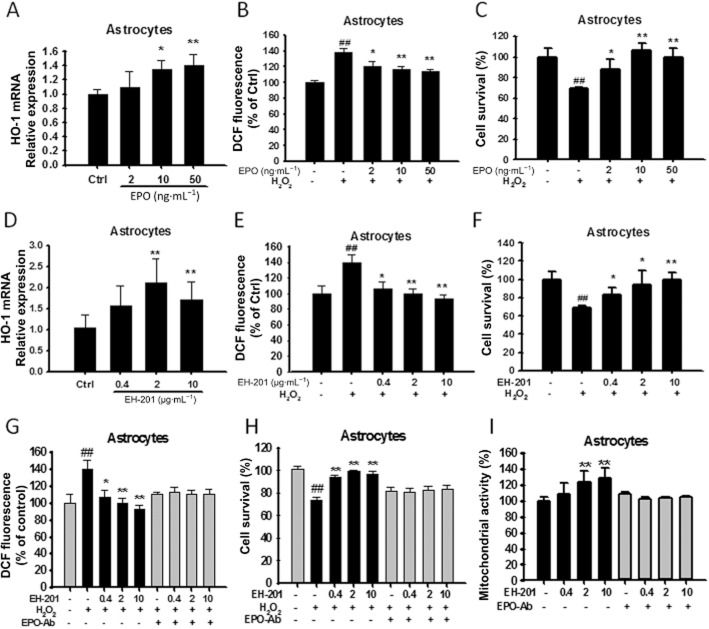
Figure 3.
EH-201 stimulated antioxidant gene (HO-1) expression, decreased intracellular ROS and attenuated H2O2-induced cell toxicity in primary astrocytes. (A, D) EPO or EH-201 treatment for 24 h increased HO-1 mRNA expression in primary astrocytes. The expression of GAPDH was used as an internal control. The results are expressed as the relative index of untreated controls means ± SD of at least three independent measurements. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01; compared with untreated controls; one-way anova followed by Tukey's multiple comparison test. (B, E) Astrocytes treated with EPO or EH-201 for 24 h were exposed to 100 μM H2O2 for 6 h. Intracellular ROS formation was measured using a DCFH-DA assay. The graph shows the results in relative percentage of fluorescence units to the control. The values indicate the means ± SD (n = 8). (C, F) Astrocytes treated with EPO or EH-201 for 24 h were exposed to 500 μM H2O2 for 6 h. Cell survival was analysed with Trypan blue staining. The values indicate the means ± SD (n = 3). (G) Co-incubation of EH-201 with an anti-EPO antibody for 24 h resulted in the loss of the EH-201-mediated reduced ROS generation induced by H2O2, as assessed by a DCFH-DA assay (n = 8), and (H) reduced H2O2-mediated cytotoxicity, as assessed by Trypan blue staining (n = 3). The values indicate the means ± SD, ##P < 0.01 compared with untreated controls; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, compared with H2O2 controls. (I) Co-incubation of EH-201 with an anti-EPO antibody resulted in the loss of the EH-201-induced increase in succinate dehydrogenase activity, as assessed by an MTT reduction assay. The values indicate the means ± SD (n = 8), *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 compared with controls; Student's t-test.