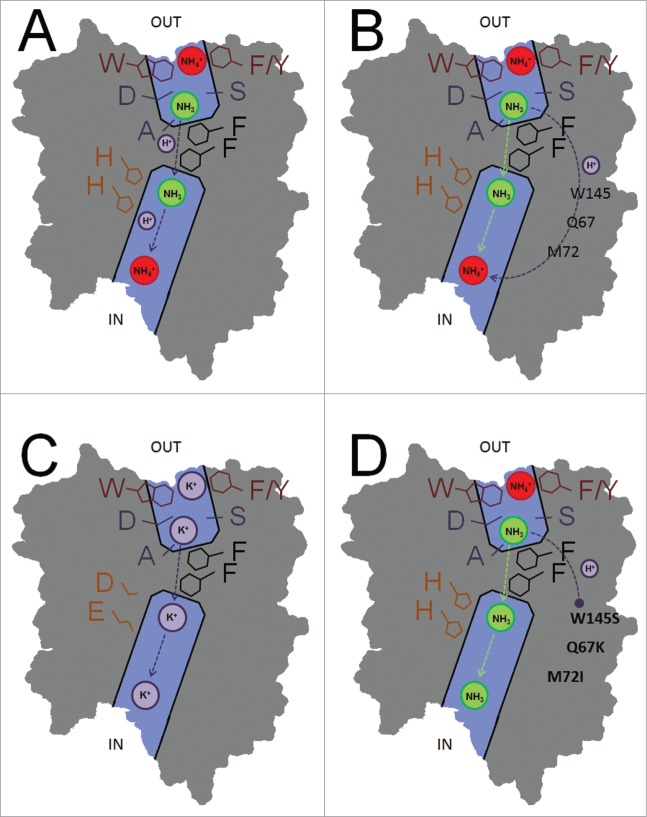
Figure 1.
Schematic transport mechanisms in AMT subunit pores. (A) Electrogenic wild type transport in which the proton is co-transported with the ammonia molecule in the central subunit pore. (B) Wild type electrogenic transport in which the proton is transported through the protein via a specific (unknown) proton pathway. (C) Mutation of the 2 pore-lining histidines in E.c. AmtB results in direct K+ transport. (D) Mutations at the subunit interfaces disrupt proton transport in A.t. AMT1;2, which results in net NH3 transport.