Figure 2.
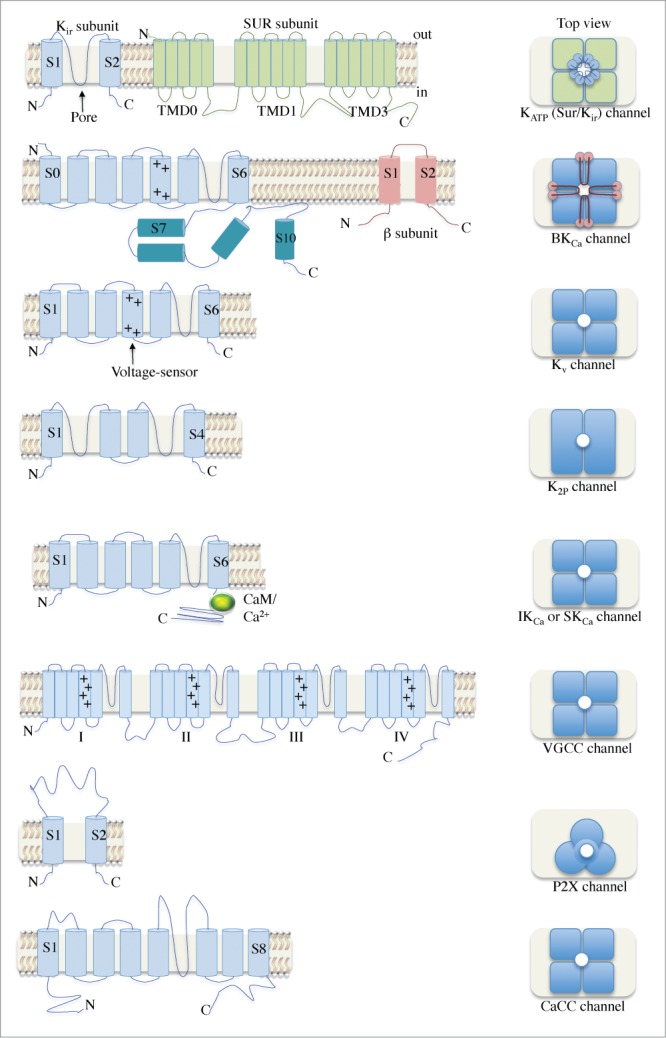
A schematic illustration of the various ion channels identified in urethral smooth muscle. The architecture of the transmembrane α and β subunits is shown in the left panel. Dimeric and trimeric arrangements can be seen for K2P and P2X channels, respectively. Most channels have tetrameric structures and several have β subunits associated. Abbreviations: N, amino-terminus; C, carboxyl-terminus; Kir, inwardly-rectifying K+ channel; SUR, sulfonylurea; TMD, transmembrane domain; KATP, ATP-sensitive K+ channel; +, positively-charged residues; BKCa, large conductance, Ca2+-activated K+ channel; Kv, voltage-gated K+ channel; CaM, calmodulin; K2P, 2-pore domain K+ channel; IKCa, intermediate conductance K+ channel; SKCa, small conductance K+ channel; VGCC, voltage-gated Ca2+ channel; CaCC, Ca2+-activated Cl− channel.
