Figure 1.
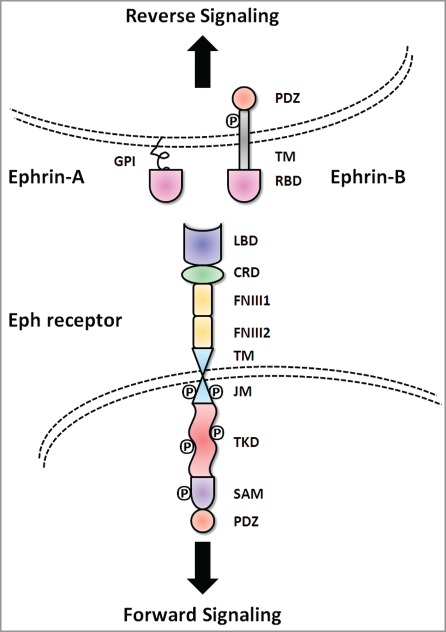
Basic molecular domain structure of Eph receptors and ephrin ligands. Eph receptors have conserved structures and domains. TheN-terminal extracellular region consists of a ligand binding domain (LBD), an epidermal growth factor-like motif within a cysteine-rich domain (CRD) and two fibronectin-type III repeats (FN III1 and FN III2). The receptors pass through the membrane via a single transmembrane domain (TM). The intracellular C-terminus starts with a juxtamembrane region (JM), followed by a tyrosine kinase domain (TKD), sterile α motif (SAM) and a PDZ (postsynaptic density protein 95, discs large 1, and zonula occludens-1) binding motif. The ephrin ligands share a conserved extracellular, N-terminal receptor binding domain (RBD). Ephrin-A ligands are attached to the cell membrane with a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchor. In contrast, ephrin-B ligands have a C-terminal tail that extends into the cytoplasm of the ligand-bearing cell through a TM domain. The C-termini of ephrin-B ligands contain a cytoplasmic tail with a PDZ binding motif.
