Figure 2.
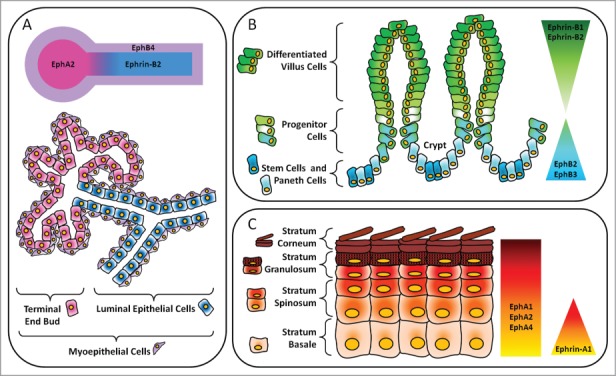
Layout of major Eph receptors and ephrin regulators in epithelial compartments. (A) Mammary gland. In the luminal epithelial cells lining the ducts, there is expression of ephrin-B2. Adjacent myoepithelial cells express EphB4. EphA2 is expressed in the terminal end bud. (B) Gastrointestinal tract. In the intestines, there is an inverse gradient of EphB and ephrin-B expression along the crypt-villous axis. EphB2 and EphB3 are important for maintenance of stem, progenitor and Paneth cells in the crypts. In the villi, ephrin-B1 and ephrin-B2 maintain the segregation of differentiated cells in the upper regions from precursor cells in the lower regions. (C) Epidermis. Ephrin-A1 is expressed in the progenitor layer, or stratum basale, of human epidermis while EphA1, EphA2 and EphA4 are present throughout all layers and are especially concentrated in the more differentiated suprabasal layers.
