Fig. 2.
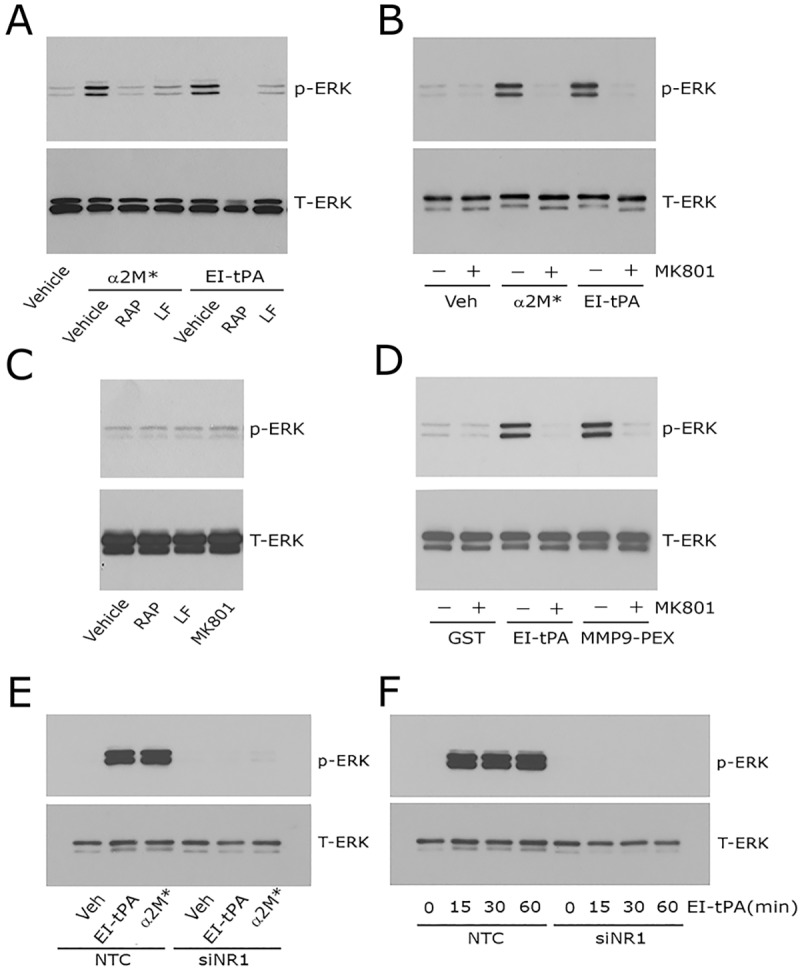
Neutralizing the NMDA-R blocks ERK1/2 activation in response to LRP1 ligands in Schwann cells. (A) Primary cultures of Schwann cells were pre-treated with 150 nM GST–RAP (RAP), 150 nM lactoferrin (LF) or with vehicle (PBS) for 30 min and then with α2M* (10 nM) or EI-tPA (12 nM) for 10 min. (B) Schwann cells were pre-treated with 1 µM MK801 (+) or with vehicle (−) for 30 min and then with α2M* (10 nM), EI-tPA (12 nM) or vehicle (PBS) for 10 min. (C) Schwann cells were treated with GST–RAP (150 nM), lactoferrin (150 nM) or MK801 (1 µM) for 30 min. (D) Schwann cells were pre-treated with 1 µM MK801 (+) or with vehicle (−) for 30 min and then with GST (20 nM), EI-tPA (12 nM), or GST–PEX (20 nM) for 10 min. (E) Schwann cells in which NR1 was silenced and control cells transfected with NTC siRNA were treated with EI-tPA (12 nm) or α2M* (10 nM) for 10 min. (F) Primary cultures of Schwann cells in which NR1 was silenced and control cells transfected with NTC siRNA were treated with EI-tPA (12 nm) for various times up to 1 h. Equal amounts of cellular protein (40 μg) were loaded into each lane and subjected to SDS-PAGE. Immunoblot analysis was performed to detect phosphorylated ERK1/2 (p-ERK) and total ERK1/2 (T-ERK). Each blot represents 3–5 independent studies.
