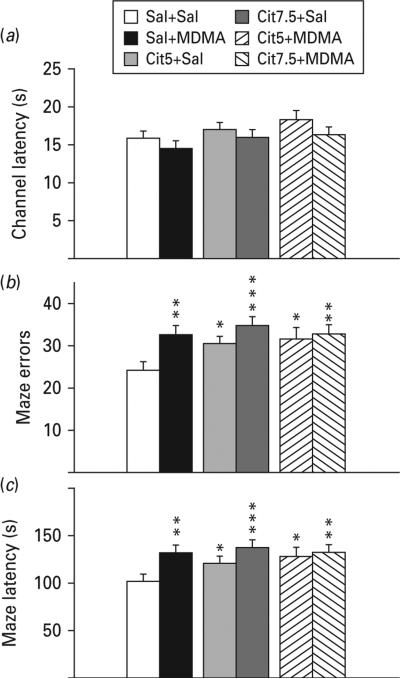
Fig. 1.
Straight swim channel and Cincinnati water maze (CWM). (a) Pre-maze trials in a 244 cm long straight swimming channel. There were no differences in latency to reach the platform during straight channel trials reflecting equivalent motoric ability and motivation to escape. (b) CWM errors of commission: number of incorrect stem, arm and start return errors in the maze. Errors were significantly increased in all groups compared to Sal+Sal. (c) CWM escape latency: time to find the escape platform in the maze. Latency was increased in all groups compared with Sal+Sal. Group comparisons were by planned false discovery rate (FDR) comparisons. * p<0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001 compared to Sal+Sal; n=16–27 per group (males) from 27 different litters; not more than one rat per group from any one litter was used to control for litter effects. Cit5, 5 mg/kg citalopram; Cit7.5, 7.5 mg/kg citalopram; MDMA, 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine; Sal, saline.