Fig 7. Sso activity is important for maintenance of ICEBs1 after excision in growing cells.
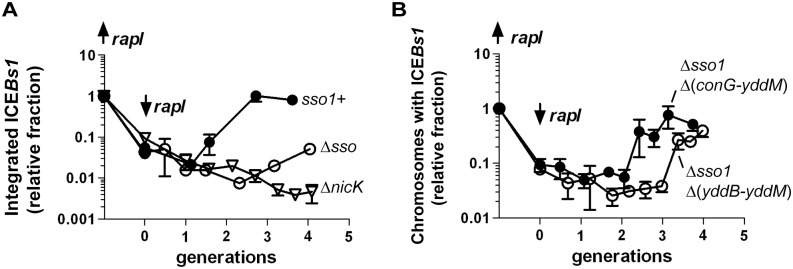
The relative fraction of cells with ICEBs1 integrated in its attachment site in the chromosome is plotted versus the number of generations after repression of Pxyl-rapI. Cells were grown in defined minimal medium with arabinose as carbon source. Xylose was added during mid-exponential phase to induce expression of Pxyl-rapI (origin on y-axis; up rapI), thereby causing induction and excision of ICEBs1. In all cases, ≥90% of cells had ICEBs1 excised from the chromosome two hours after induction of Pxyl-rapI. Two hours after addition of xylose, cells were pelleted and resuspended in glucose to repress expression of Pxyl-rapI (time = 0 generations; down rapI). Samples were taken for determination of the relative fraction of cells with ICEBs1 integrated in the chromosome generating attL, the junction between chromosomal sequences and ICEBs1. Data presented are from one representative experiment of at least three independent experiments. Error bars indicate the standard deviation of technical triplicates. (A) Data for mini-ICEBs1 with (sso1+; filled circles; strain LDW131) or without (Δsso; open circles; strain LDW180) sso1. ΔnicK (open triangles; strain CAL1215) is an ICEBs1 mutant that is unable to replicate autonomously and is lost from the population of cells after excision from the chromosome and continued cell growth and division [30]. (B) Data are for the indicated deletion derivatives of ICEBs1, both missing sso1 and the indicated regions: Δsso1 Δ(conG-yddM) (filled circles; strain LDW87) and the derivative missing a bit more of ICEBs1, Δsso1 Δ(yddB-yddM) (open circles; strain LDW89). Maps of the ICEBs1 mutants are in Fig 1.
