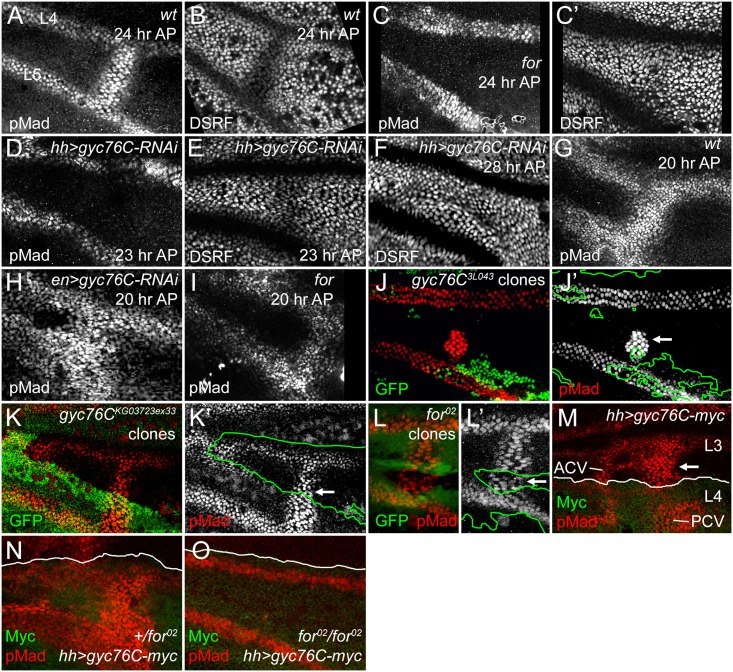
Fig 3. For and Gyc76C are required for the refinement and maintenance of BMP signaling.
(A,B) PCV regions of 24 hour AP wild type (wt) wings showing anti-pMad staining (A) and suppression of anti-DSRF expression (B) in veins. (C,C’) 24 hour AP for 02 homozygote wing showing loss of loss of pMad (C) and failure to suppress DSRF (C’) in PCV. (D,D) 23 hour AP hh-Gal4 UAS-gyc76C-RNAi wings showing loss of pMad (D) but still slight suppression of DSRF (E) in PCV. (F) 28 hour AP hh-Gal4 UAS-gyc76C-RNAi wing showing failure to suppress DSRF in PCV. (G) Anti-pMad staining in 20 hour AP wild type wing. (H) 20 hour AP en-Gal4 UAS-gyc76C-RNAi wing showing abnormally broad anti-pMad in PCV and LVs. (I) 20 hour AP for 02 homozygous wing showing pMad in PCV. (J-K’) Anti-pMad staining (red, white) in homozygous gyc76C 3L043 (J,J’) or gyc76C KG0372ex33 (K,K’) clones (identified by absence of green GFP) in 28 hour AP hs-FLP/+; gyc76C FRT 2A /hs-GFP RpS17 4 FRT 2A wings. Individual cells in PCV retain high levels of pMad (arrows), similar to levels in neighboring wild type PCV or LV cells. (L,L’) Normal anti-pMad staining (red, white) in PCV cells of homozygous for 02 clone (identified by absence of green RFP) in hsFlp; for 02 FRT 40A/ubi-RFP FRT 40A 26 hour AP wing. (M) Anti-pMad (red) and anti-Myc (green) staining in a 24 hour AP UAS-myc-gyc76C/+; hh-Gal4/+ wing. Arrow indicates ectopic pMad between L3 and L4 anterior to the PCV, outside the region of hh-Gal4-driven expression of Myc-Gyc76C. (N,O) Comparison of anti-pMad (red) staining in 25 hour +/for 02 and for 02/for 02 wings with hh-Gal4 UAS-gyc76C-myc/+ (anti-Myc, green). Ectopic pMad observed in for heterozygote (N) is lost in for homozygote (O).