Fig. 1.
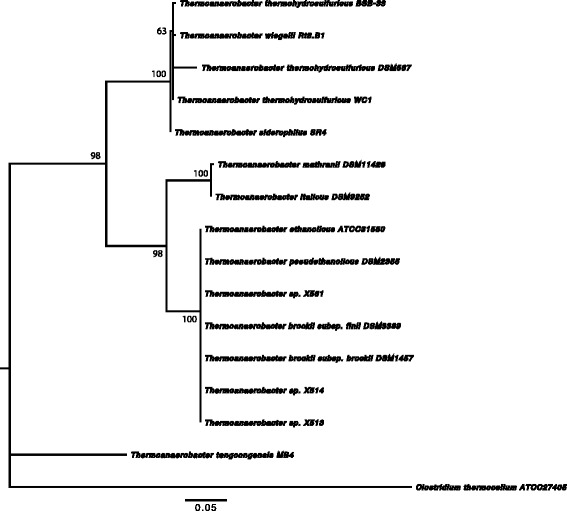
Phylogenetic tree highlighting the position of Thermoanaerobacter thermohydrosulfuricus BSB-33 relative to other type strains within the Thermoanaerobacteraceae. The tree was inferred from aligned characters of the cpn60 UT sequences using maximum likelihood method within the software MEGA v5.1 (bootstrap: calculated with the Kimura 2-parameter model distance correction and 1000 replicates). The strains and their corresponding GenBank accession numbers for cpn60 UT genes are: T. wiegelii Rt8.B1, JGI; T. thermohydrosulfuricus WC1, HM623896; T. thermohydrosulfuricus BSB-33, JGI; T. thermohydrosulfuricus DSM567, HM623910; T. siderophilus SR4, JGI; T. mathranii DSM11426, DQ439966; T. italicus DSM9252, NZ_ACVH01000076; T. ethanolicus ATCC31550, NZ_ACXY01000003; T. brockii subsp. finii DSM3389, NZ_ACQZ01000003; T. brockii subsp. brockii DSM1457, HM623909; Thermoanaerobacter sp. X513, ACPF01000040; Thermoanaerobacter sp. X514, NC_010320; T. pseudethanolicus DSM2355, NC_010321; Thermoanaerobacter sp. X561, ACXP01000037; T. tengcongensis MB4, NC_003869; Clostridium thermocellum ATCC27405, NC_009012. Bootstrap values are indicated at nodes when larger than 60 %. Clostridium thermocellum was used as an out group. The branches are scaled in terms of the expected number of substitutions per site (scale bar)
