Fig 2.
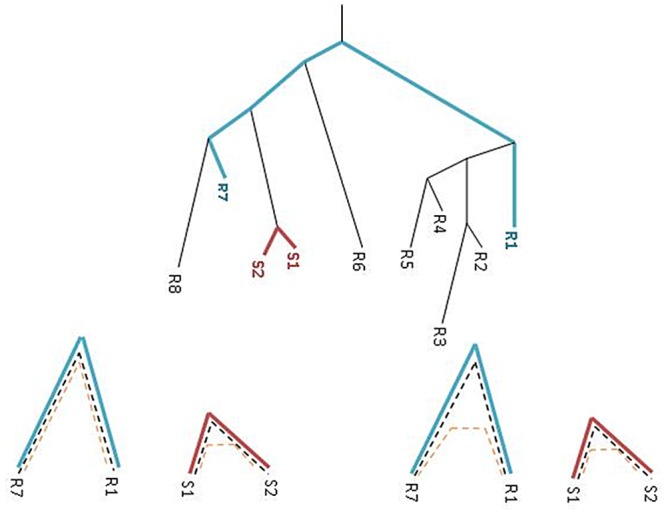
Top: The phylogeny over a group of organisms with branch lengths proportional to distances of gene g h. g h has undergone HGT between the two strains S 1 and S 2 and hence their distance is very short compared with two reference organisms R 1 and R 7. Bottom: The reference gene (blue, dashed line) must be a gene that accumulates mutations ever since the divergence of both the strains and reference organisms. There are two cases in which the suspicious gene evolves at the reference organism. (A) No HGT and then the constant relative conserveness is maintained (black dashed). (B) HGT of the SI suspicious gene at the reference organisms and the constant relative conservation is not maintained (yellow dashed).
