Fig. 2.
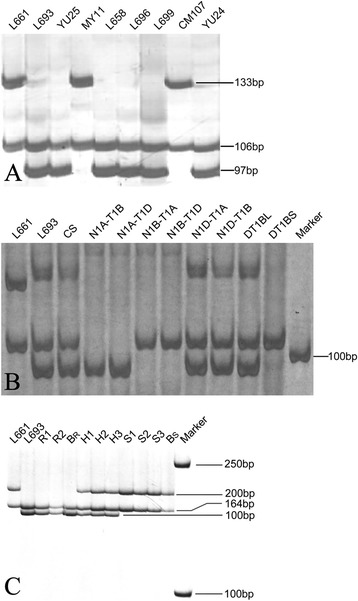
Identification of polymorphism between stripe rust-resistant and stripe rust-susceptible genotypes. The Ls36 primer designed from an EST sequence [GenBank: JK972238] produced polymorphic amplicons among the various genotypes. a a 133 bp amplicon was amplified in the susceptible L661 line and its susceptible parents MY11 and CM107. A 97 bp amplicon was amplified in resistant L693 line, resistant sister lines L658, L696, and L699, and their resistant parent, YU25. A 97 bp amplicon was also amplified from YU24, one of the resistant sister lines of YU25. A 106 bp fragment was amplified in all genotypes. b chromosomal localizations of the amplicons that were polymorphic between L693 and L661, with CS nulli-tetrasomic lines of homoeologous group 1 and ditelosomic lines of wheat chromosome 1B. PCR was performed to map the gene using genomic DNA from the CS and various aneuploids. PCR products were resolved on 6 % polyacrylamide gels. No PCR product was generated from nullisomic 1B (N1BT1A and N1BT1D) or the ditelosomic 1BS (DT1BS) lines. c Silver-stained polyacrylamide gels showing polymorphic markers generated using the LSc18 primer linked to the stripe rust resistance gene in L693. L661, susceptible parent; L693, resistant parent; R1 and R2, resistant F2 individuals; BR, the resistant F2 DNA pool; H1, H2 and H3, resistant F2 individuals; S1, S2 and S3, susceptible F2 individuals; BS, the susceptible F2 DNA pool. L661, S1, S2, S3 and Bs showed amplification of 173 bp and 200 bp fragments; L693, R1, R2 and BR showed amplification of 164 bp and 173 bp fragments; H1, H2 and H3 showed amplification of all three fragments, indicating heterozygosity
