Fig. 5.
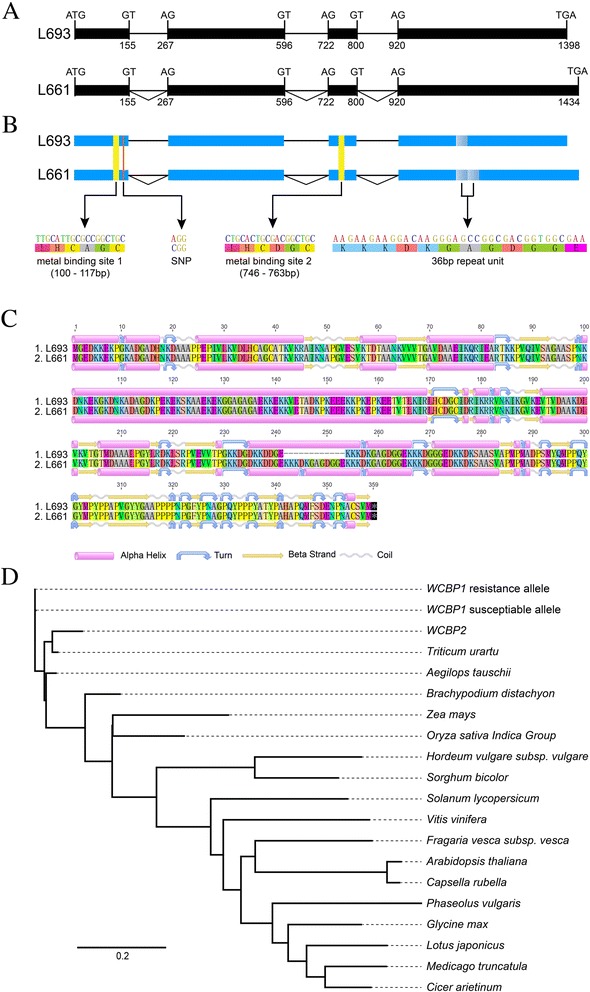
The WCBP1 gene, its putative protein structure, and its phylogenetic tree. a The predicted mRNA structure of WCBP1 is shown above the genomic sequence, including introns (thin lines) and exons (thick lines). ATG represents the methionine start codon, and TGA represents the stop codon. b Coding regions of two heavy metal copper-binding domains in exons 1 and 3. The major differences between the resistance-and susceptibility-associated WCBP1 alleles are a SNP in exon 1 and a 36 bp deletion in exon 4. c Alignment of the amino acid sequences and secondary structures of the proteins putatively encoded by the resistance-and susceptibility-associated alleles of WCBP1. d Phylogenetic tree constructed using the neighbor-joining algorithm in MEGA 5.05 following WCBP1 protein sequence alignment using the CLUSTALW program. Accession numbers for the other heavy metal copper-binding proteins were as follows: EMS53947 (Triticum urartu) (11.37 %), EMT15307 (Aegilops tauschii) (11.37 %), XP_003573974 (Brachypodium distachyon) (11.37 %), EAY78671 (Oryza sativa indica group) (3.72%), XP_002465840 (Sorghum bicolor) (6.65 %), AFK36536 (Medicago truncatula) (4.72 %), XP_004497534 (Cicer arietinum) (4.72%), XP_004955283 (Setaria italica) (4.58 %), BAK03814 (Hordeum vulgare subsp. vulgare) (4.15 %), XP_004304460 (Fragaria vesca subsp. vesca) (4.01%), DAA49855 (Zea mays) (3.93 %), NP_195958 (Arabidopsis thaliana) (3.79 %), EOA20845 (Capsella rubella) (3.79 %), XP_004246628 (Solanum lycopersicum) (3.72 %), XP_003542527 (Glycine max) (3.72 %), AFK35929 (Lotus japonicus) (3.72 %), EAY78671 (Oryza sativa indica group) (3.72%), XP_002276537 (Vitis vinifera) (3.72%) and AFW90521 (Phaseolus vulgaris) (3.29 %)
