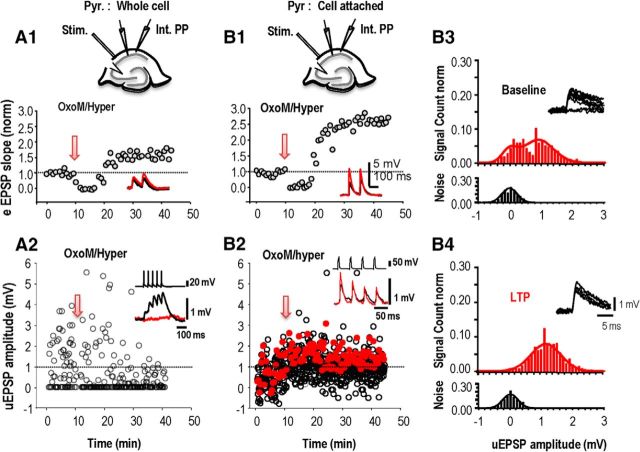
Figure 8.
Long-term potentiation of unitary EPSCs induced in oriens interneuron. Responses of an interneuron to fiber stimulation in stratum oriens (A1, B1) were recorded in parallel with unitary events evoked by a CA1 pyramidal cell (A2, B2) before and after activation of mAChRs (OxoM). The presynaptic pyramidal cell was recorded in whole-cell mode (A) or in cell-attached mode (B) to avoid the cytoplasm dialysis. A1, EPSPs induced in the interneuron by fiber stimulation were depressed before a long-term potentiation emerged. A2, From the same experiment as A1, unitary EPSPs induced in the interneuron showed a maintained depression when CA1 pyramidal cell action potentials were induced in whole-cell recording mode. B1, Sequence of depression followed by long-term potentiation of afferent EPSPs induced by activation of mAChRs (OxoM). B2, Same experiment as B1, unitary EPSPs showed a maintained potentiation when CA1 pyramidal cell action potentials were induced in a cell-attached record. A1 and B1 show EPSP slope averaged >20 events elicited at 15 s intervals. A2 and B2 show amplitudes of all unitary EPSPs evoked at 15 s intervals. B3, B4, Amplitude distributions for unitary events (red, top) elicited in an interneuron by pyramidal cell action potentials and of the noise (black, bottom) measured as described in Materials and Methods. Data were obtained from 256 trials at −15 to 0 min before and from 640 trials at 20–40 min after the potentiation protocol. A Gaussian fit to the noise amplitude had a mean of 0.03 ± 0.23 mV before and 0.01 ± 0.24 mV after potentiation. From a double-Gaussian fit to events evoked by action potentials, the proportion of failures was reduced from 0.205 to 0.002. The synaptic efficacy, or amplitude of evoked EPSPs, was 0.8 ± 0.4 mV before and 1.27 ± 0.7 mV after plasticity was induced. Insets in B3 and B4 show overlays of 10 responses induced before and after LTP.