Figure 4. Effects of putative CRP binding sites on the tfoXVC expression.
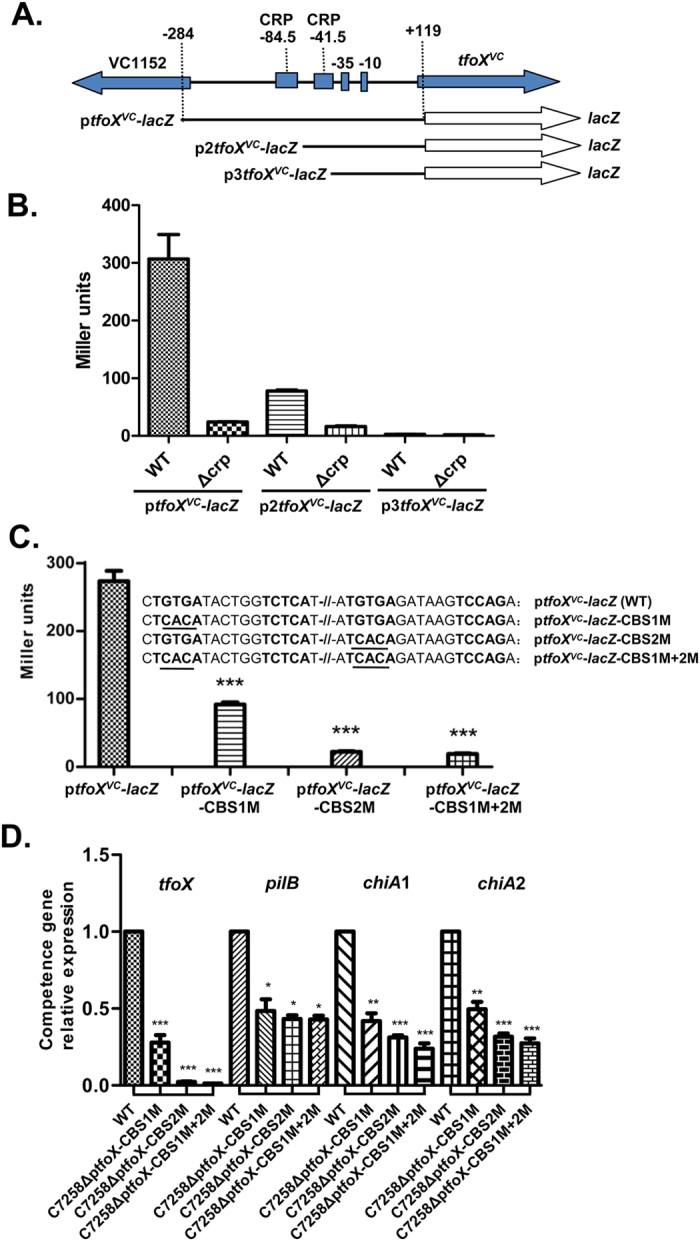
(A) The structural organizations of the tfoXVC promoter and transcriptional fusions. Two putative CRP binding sites were found in the upstream region of tfoXVC centered at positions −84.5 and −41.5. (B) A deletion analysis of the tfoXVC promoter. V. cholerae strains C7258∆lacZ (WT) and WL7258∆lacZ (∆crp) containing the p2tfoXVC–lacZ and p3tfoXVC–lacZ fusion, respectively, were grown at 37 °C to mid-log phase. (C) The promoter activities of wild-type and CBS mutated fusions. C7258∆lacZ containing ptfoXVC–lacZ, ptfoXVC-lacZ-CBS1M, ptfoXVC-lacZ-CBS2M, or ptfoXVC-lacZ-CBS1M+2M were grown at 37 °C to the mid-log phase. The β-galactosidase activity was measured as described in the Methods. The mutated bases in fusions were constructed by site-directed mutagenesis and underlined. (D) V. cholerae strains C7258 (WT), C7258∆ptfoX-CBS1M, C7258∆ptfoX-CBS2M and C7258∆ptfoX-CBS1M+2M were grown in LB medium to late-log phase. The tfoXVC and pilB, chiA-1 and chiA-2 mRNA abundances were measured by qRT-PCR. Error bars indicate the standard deviations of three independent cultures. The “WT” bar was set to 1 and used as a reference to calculate subsequent expression values. ***Significantly different from the wild-type strain (t-test, P < 0.0003). *Significantly different from the wild-type strain (t-test, P < 0.05).
