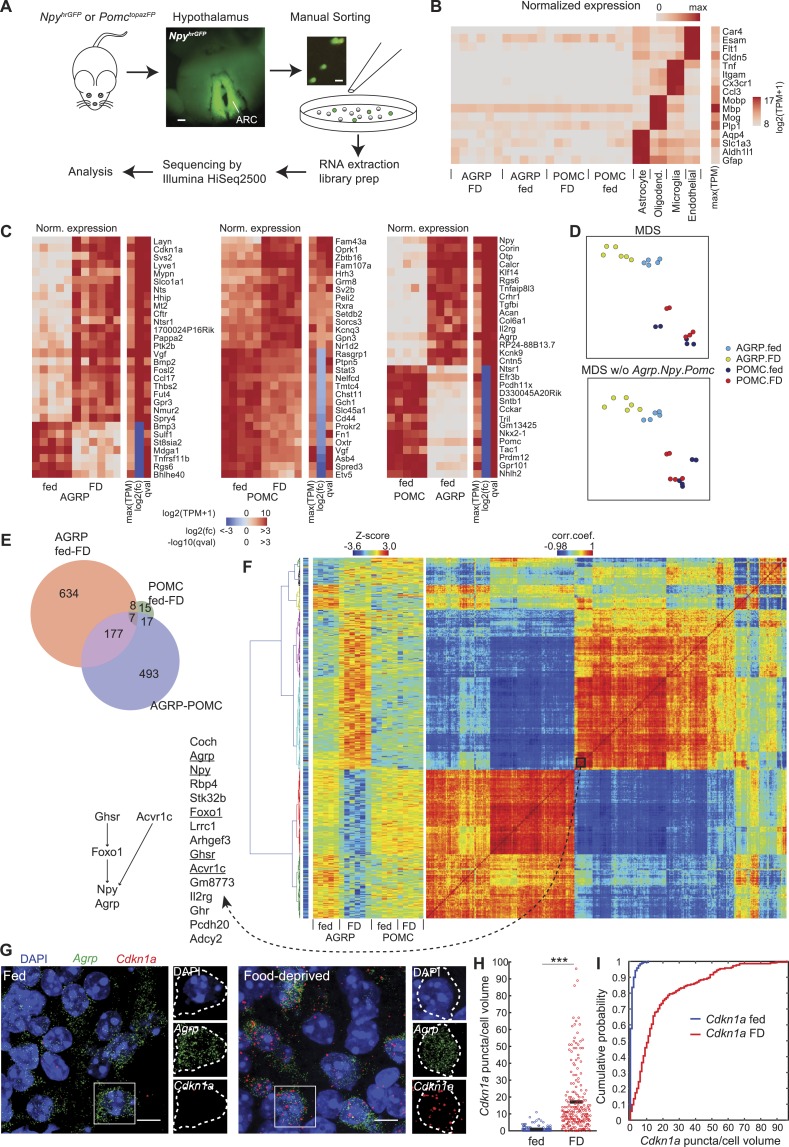
Figure 1. Cell type-specific transcriptomic profiling of starvation-sensitive neurons.
(A) Schema for dissection and sorting of fluorescent neurons from the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus (ARC) followed by cell type-specific RNA-Seq. Scale: ∼200 µm (left), ∼20 µm (right). (B) Expression levels of marker genes for astrocytes, myelin oligodendrocytes, microglia, and endothelial cells indicate high purity of AGRP and POMC samples. FD: 24-hr food-deprived. Left, for each sample, log expression levels for a single gene in each row normalized by maximum expression level of the transcript in any of the samples. Right, sidebar shows maximum expression level for each row (each transcript) across all samples. TPM: transcripts per million. (C) Top 30 differentially expressed genes (DEG) for: AGRP neurons, FD/fed; POMC neurons, FD/fed; AGRP/POMC neurons (fed). FD: 24-hr FD. As in (B), each row corresponds to a transcript where the expression level in each sample is normalized by maximum expressions on level in the row. The sidebars show maximum expression level [max(TPM)] across samples in each row (each transcript). In addition, log2(fold-change) [log2(fc)], and q-value (qval) for the differential expression across fasted/fed states (left and middle) or AGRP/POMC expression levels are shown. (D) Top, multidimensional scaling (MDS) projection of distance (1-corr.coef.) between samples. Bottom, MDS without Agrp, Npy and Pomc genes in the calculation. (E) Venn diagram for DEG between FD and fed conditions (AGRP FD-fed: red, POMC FD-fed: green) and between AGRP and POMC neurons (both fed, purple). Reported DEG required q-value <0.05, abs[log2(fc)] > 1 and mean CPM > 20 in at least 1 cell type/condition (see ‘Materials and methods’). (F) Hierarchical clustering of DEG. Matrix in the middle indicates standardized expression level for the samples (columns) and DEG (rows). The matrix on the right shows the correlation coefficients between genes, calculated across all samples. The colormap on the left indicates maximum TPM expression level in log2 scale, which ranges from 2.96 (blue) to 15.6 (red). Left, genes in a cluster that comprise known pathways that regulate Agrp and Npy expression. (G) Representative images of double single molecule fluorescence in situ hybridization (smFISH) for Agrp and Cdkn1a. Scale, 10 μm. (H, I) Population counts (bars: mean value) (H) and cumulative probability distributions (I) of Cdkn1a puncta per cell volume in AGRP neurons (p = 1.5e−53, Kolmogorov–Smirnov [ks]-test). ***p < 0.001. Fed, n = 189 cells; FD, n = 215 cells; 3 mice per condition.