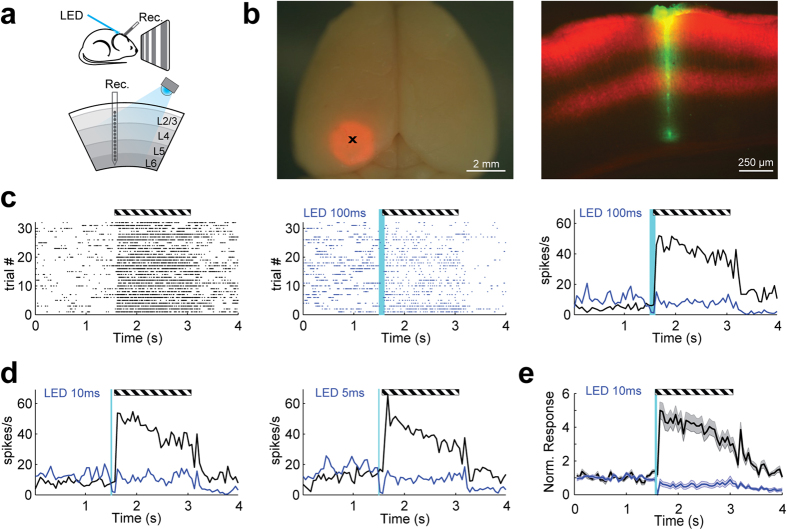
Figure 7. In vivo suppression of sensory evoked spikes by iChloC.
(A) Schematic representation of the experimental setup. Drawing by R. Beltramo and M. Scanziani. (B) Left panel: Epifluorescence image of a mouse brain expressing iChloC (red) in V1. The black ‘x’ indicates the penetration site of the extracellular electrode that recorded the spikes shown in (C). Right panel: Epifluorescence image of coronal section through V1 of the brain shown on the left. Red: Viral expression of iChloC; Green: Recording site. (C) Extracellular recording from V1 in response to visual stimulation (full-field drifting gratings) under control conditions (black raster plot of multi-unit activity, left panel) and following 100 ms of iChloC photoactivation (blue raster plot, central panel). Control and photostimulation trials were interleaved. Right panel: Average peri-stimulus time histograms (PSTH, binning 50 ms) of control (black) and photostimulation (blue) trials. Striped horizontal bar indicates visual stimulus duration (1.5 s). Vertical cyan line: iChloC photoactivation (100 ms). (D) Same as in (C) for iChloC photostimulation of 10 ms and 5 ms durations. (E) Baseline normalized average PSTH (solid lines) and standard errors (shaded areas) of cortical responses to drifting gratings with (blue) and without (black) iChloC photoactivation (10 ms), from 4 tetrodes in 2 animals.