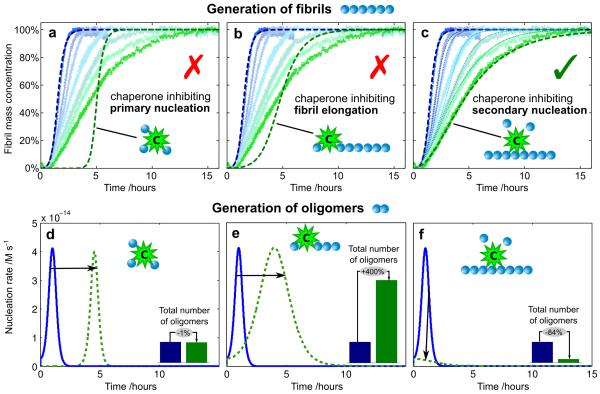
Figure 1. Kinetics of Aβ42 aggregation in the presence of Brichos.
(a-c) Reaction profiles from left (blue) to right (green) for aggregation in the absence of Brichos and in the presence of 10%, 15%, 35%, 50%, 75%, and 100% Aβ42 monomer equivalents of Brichos. The data show averages (points) and standard errors over five technical replicas. The effect of Brichos saturates at a stoichiometry of approximately one monomer equivalent of Aβ42 (see Supplementary Fig.1). The blue dashed line is the integrated rate law for Aβ42 aggregation in the absence of Brichos using the rate constants determined previously19. The green dashed lines show predictions for the resulting reaction profiles when each of (a) primary nucleation, (b) fibril elongation, and (c) secondary nucleation are inhibited by the chaperone (see Supplementary Fig. 2). The thin dotted lines in (c) are theoretical predictions for the reaction profiles at the intermediate Brichos concentrations using the association and dissociation rate constants determined for its binding by means of SPR (Fig. 3b). (d-f) Time evolution of the nucleation rate calculated from the kinetic analysis. The blue line corresponds to the situation in the absence of Brichos and the green dashed lines show predictions for the cases when each of (d) primary nucleation, (e) fibril elongation, and (f) secondary nucleation are inhibited by the chaperone. The insets show the relative number of oligomers generated during the aggregation reaction. The concentration of monomeric Aβ42 was 3μM.