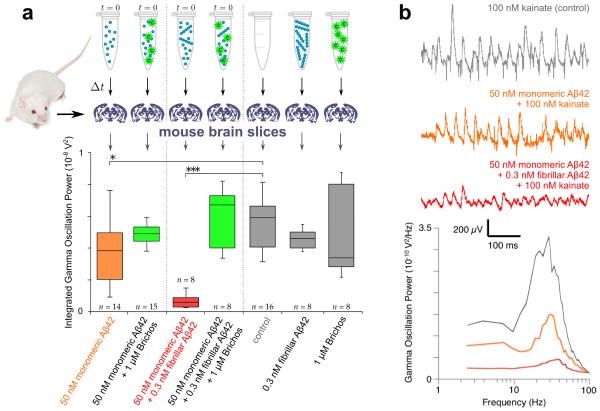
Figure 5. Brichos reduces the toxicity associated with the aggregation of Aβ42 in brain slices.
(a) Solutions containing mature fibrils alone and chaperone alone do not show increased toxicity relative to the control (first gray bar, p = 0.3 and p = 0.5). The toxicity is, however, increased relative to the control for solutions (Δt = 15 min) undergoing aggregation from initially purely monomeric peptide (orange bar, p = 0.02, indicated *), and is furthermore dramatically increased in samples initially containing monomeric Aβ42 with pre-formed fibrils (red bar, p < 0.0001, indicated ***). In both of these aggregation reactions, the toxicity is strongly suppressed to a level comparable with the control by adding Brichos in solution (green bars, p = 0.3 and p = 0.2 relative to the control). The box-and-whisker plot is based on 8-16 repeats for each condition as indicated, with the boxes enclosing data from the first to the third quartile, the horizontal line being drawn at the median, the whiskers indicating the range, and the number of repeats given above or below. All p-values are based on two-tailed Mann-Whitney U-tests relative to the control. (b) Representative traces and power spectra of the kainate-induced gamma oscillation measurements for the control (gray), the monomeric peptide (orange) and the monomeric peptide supplemented with pre-formed fibrils (red).