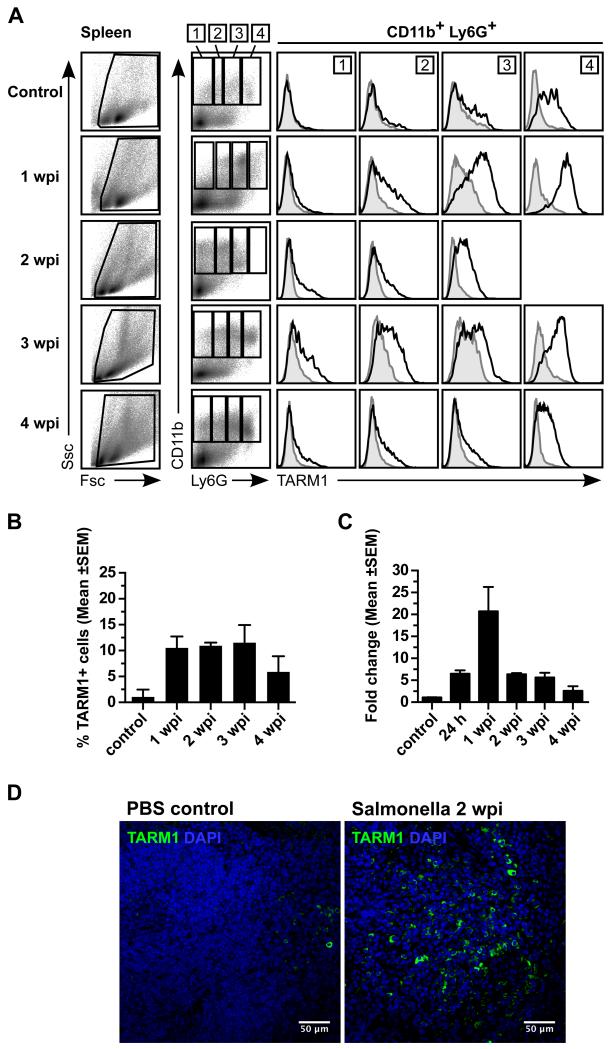
FIGURE 7.
Systemic infection with S. Typhimurium causes upregulation of TARM1 expression by CD11b+Ly6G+ neutrophils and their accumulation in the spleen. C57BL/6 mice (n=3) were injected i.v. with either PBS or aroA attenuated S. Typhimurium strain SL3261 (1 × 106 CFU) and sacrificed at the indicated time points. TARM1 expression was determined by flow cytometry, qPCR and confocal microscopy. Representative plots from one of three independent experiments are shown. (A) Flow cytometric analysis of the expression of TARM1, CD11b and Ly6G on total splenocytes at the indicated time points following infection. CD11b+ cells were gated according to their Ly6G expression (gates 1-4). Histogram overlays show TARM1 expression in corresponding Ly6G gates. (B) Percentage of TARM1+ cells in total splenocytes at indicated time points following infection. (C) qPCR analysis of TARM1 mRNA expression in total splenocytes over the course of infection. (D) Confocal microscopy of the spleen at 2 wpi and uninfected control. Green, TARM1; Blue, DAPI.