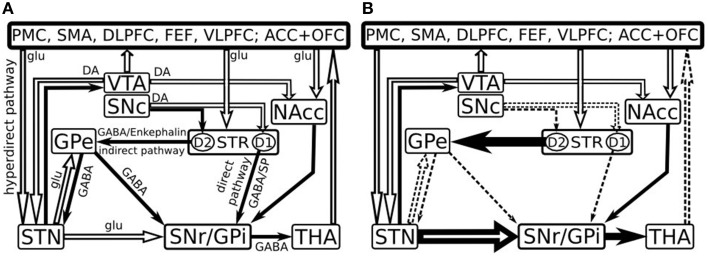
Figure 1.
Model of the basal ganglia connectivity in healthy (A) and in early Parkinson's disease (B) [Adapted after Kalivas and Nakamura (1999), Dudel et al. (2002), Nambu et al. (2002), Gubellini et al. (2009) and Cools (2006)]. Open and filled arrows represent excitatory glutamatergic (glu) and inhibitory gabaergic (GABA) projections. PMC, Premotor cortex; SMA, supplementary motor area; DLPFC, dorsolateral prefrontal cortex; FEF, frontal eye fields; VLPFC, ventrolateral prefrontal cortex; ACC, anterior cingulate cortex; OFC, orbitofrontal cortex; VTA, ventral tegmental area; SNc, substantia nigra pars compacta; SNr, substantia nigra pars reticulata; NAcc, nucleus accumbens; GPe, external segment of the globus pallidus; GPi, internal segment of the globus pallidus; STR, striatum; STN, subthalamic nucleus; THA, thalamus; DA, dopamine; SP, Substance P; D1, D1 class DA receptors; D2, D2 class DA receptors.