Figure 1.
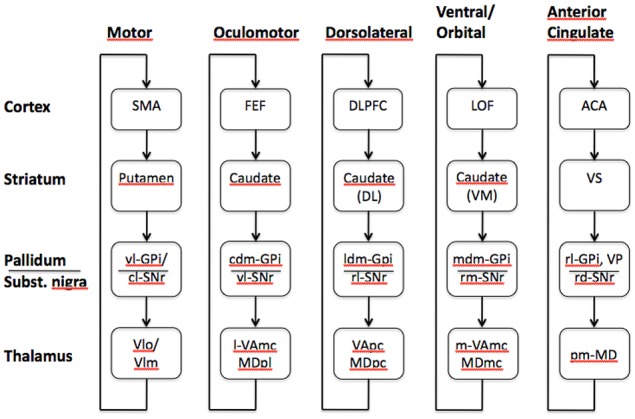
Functional loops as described by Alexander et al. (1986) involving the prefrontal cortex and the basal ganglia. Specific areas of the prefrontal cortex will interact with specific nuclei within the basal ganglia generating five closed parallel striato-thalamo-cortical loops, the dorsolateral, and motor loops involve the caudate nucleus and the putamen, respectively. The oculomotor and ventral circuits involve different areas of the caudate nucleus, while the anterior cingulate loop interacts with the ventral striatum. SMA, supplementary motor area; vl-GPi, ventrolateral-globus pallidus internal segment; cl-SNr, caudolateral substantia nigra pars reticulata; VLo, ventrolateral nucleus of the thalamus pars oralis; Vlm, ventrolateral nucleus of the thalamus pars medialis; FEF, frontal eye fields; cdm-GPi, caudodorsomedial globus pallidus internal segment; vl-SNr, ventrolateral substantia nigra pars reticulata; l-VAmc, lateral ventral anterior nucleus of the thalamus pars magnocellularis; MDpl, parvocellular subnucleus of mediodorsal nucleus of the thalamus; ldm-GPi, lateral dorsomedial globus internal segment; rl-SNr, rostrolateral substantia nigra pars reticulata; VApc, parvocellular portion of the ventral anterior thalamic nucleus; MDpc, parvocellular portion of the mediodorsal thalamic nucleus; LOF, lateral orbitofrontal cortex; Caudate (VM), ventromedial caudate nucleus; mdm-GPi, medial dorsomedial globus pallidus internal segment; rm-SNr, rostromedial substantia nigra pars reticulata; m-VAmc, medial ventral anterior nucleus of thalamus magnocellularis; MDmc, magnocellular subnucleus of mediodorsal nucleus of the thalamus; ACA, anterior cingulate area; VS, ventral striatum; rl-GPi, rostrolateral globus pallidus internal segment; rd-SNr, rostrodorsal substantia nigra pars reticulata; pm-MD, posteromedial mediodorsal nucleus of the thalamus (adapted after Alexander et al., 1986).
