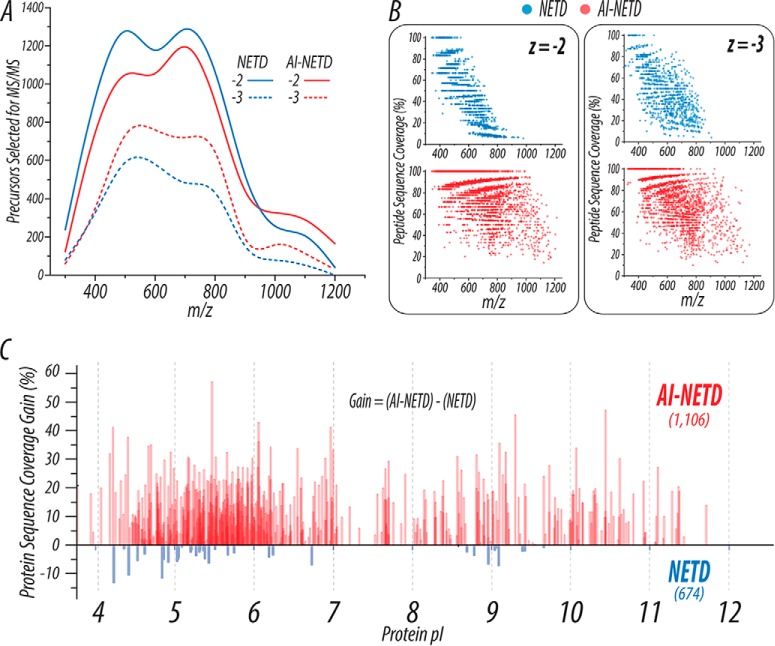
Fig. 4.
AI-NETD outperforms NETD on a global scale. (A) The distribution of precursors selected for NETD or AI-NETD in a given run show roughly equivalent populations of peptides to fragment. (B) Using the PSMs generated from the runs shown in (A), peptide sequence coverage is plotted as a function of precursor m/z. AI-NETD increases the number of peptides identified, extends the m/z range that can generate successful PSMs, and provides overall higher peptide sequence coverage at given m/z values. (C) The combination of these improvements with AI-NETD at the peptide level translates to benefits at the protein level as well. AI-NETD characterized 1,106 proteins to NETD's 674. Beyond this, for proteins detected with both methods, AI-NETD overwhelmingly enhanced protein sequence coverage, by more than 50% in some cases.