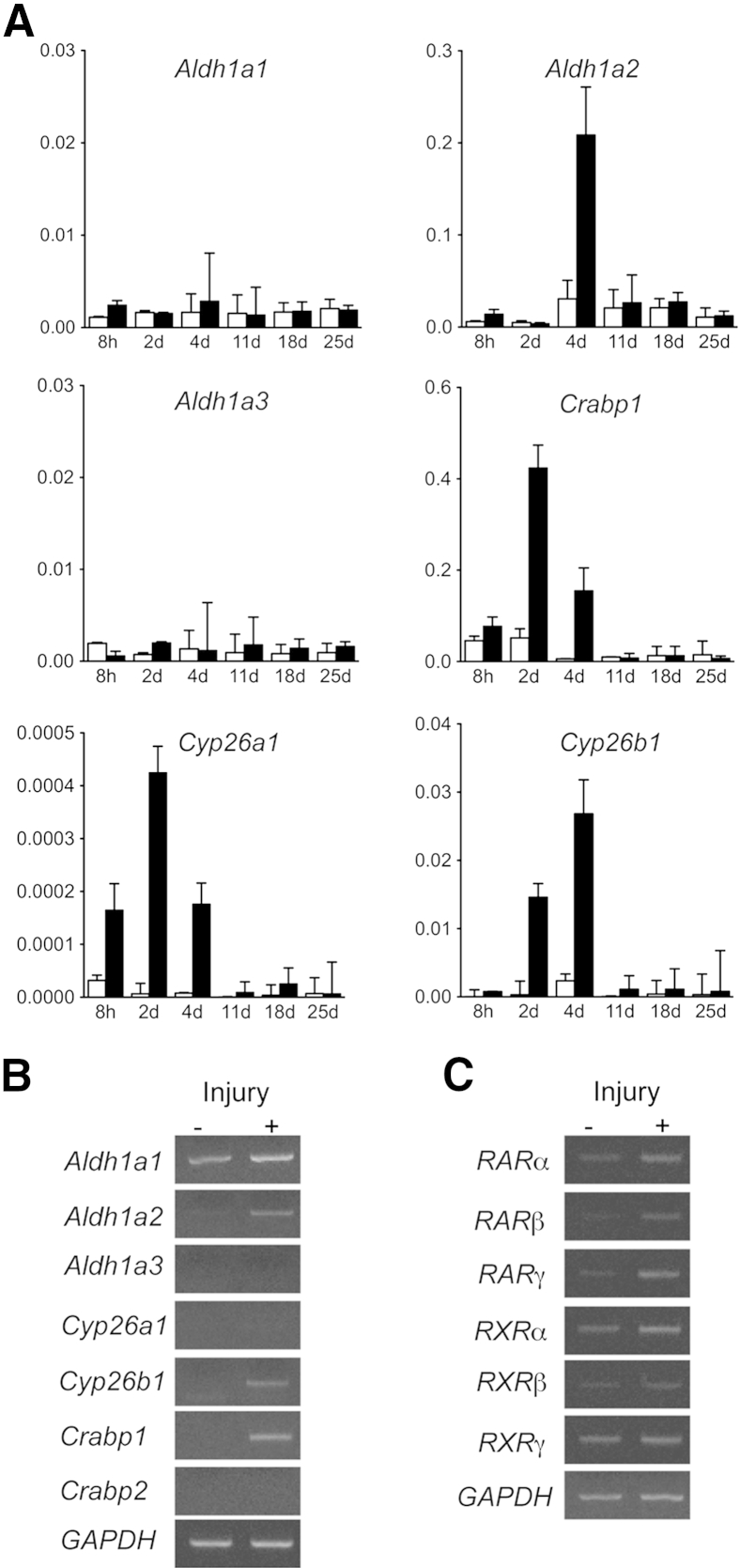
Figure 6.
Gene expression of retinoic acid metabolism–related molecules and receptors in injured and intact skeletal muscle. Lacerated muscle injury surgery (injury+, black column) or sham surgery (only skin incision, injury−, white column) was performed in 7-week-old CD1 mice (four mice per group). Muscles were harvested 8 hours and 2, 4, 11, 18, or 25 days after surgery (A) or 4 days after surgery (B and C). Total RNAs were prepared from the muscles, reverse transcribed, and subjected to real-time PCR (A) or conventional PCR (B and C). A: Changes of gene expression of retinoic acid (RA) metabolism–related enzymes after muscle injury. Graph shows relative expression levels of indicated genes to sham-operated on sample: Aldh1a1, Aldh1a2, and Aldh1a3 encode enzymes for RA biosynthesis; Crabp1 encodes an RA-binding protein; Cyp26a1 and Cyp26b1 encode enzymes that metabolize RA. B: PCR products generated with the primers that were used for real-time PCR. The results indicate specificity of these primers. C: PCR analysis of gene expression of RA receptors (RARs) in uninjured (injury−) and injured muscle (injury+). Values are means ± SD of four samples (A). d, days; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; h, hours; RXR, retinoid X receptor.