Figure 1.
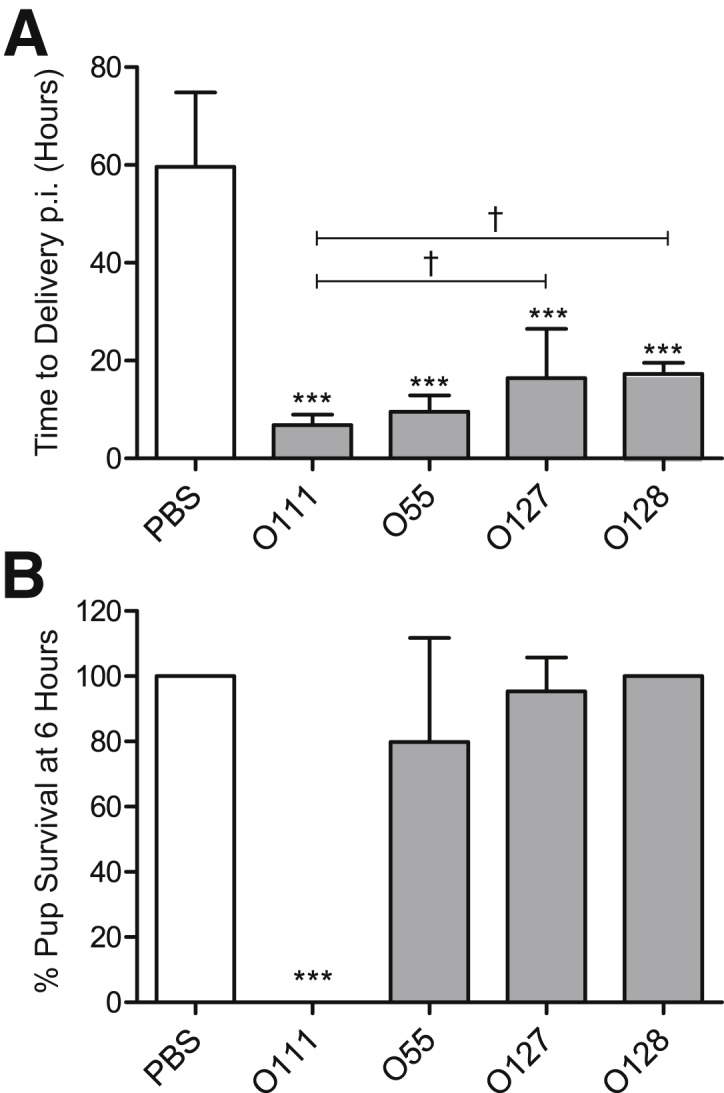
Specific Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide (LPS) serotypes induce differential maternal and neonatal outcomes in a murine model of preterm labor. A: The mean time of delivery of control dams administered an upper intrauterine injection of phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) is 60 ± 4 hours postinjection (p.i.), whereas those administered O111:B4 deliver 7 ± 1 hours p.i., O55:B5 deliver 10 ± 1 hours p.i., O127:B8 deliver 16 ± 4 hours p.i., and O128:B12 deliver 17 ±1 hours p.i. B: Pup viability rates at 6 hours postinjection are 100% for PBS and O128:B12-treated dams; however, in the case of O111:B4, all pups die at 6 hours. Pup viabilities for O55:B5 and O127:B8 serotypes are 80% and 95%, respectively. ∗∗∗P < 0.001 indicates significant differences compared with PBS-injected control dams; †P < 0.05 indicates significant differences within the LPS treatment group (one-way analysis of variance with Tukey's post hoc analysis). n = 5 (A and B).
