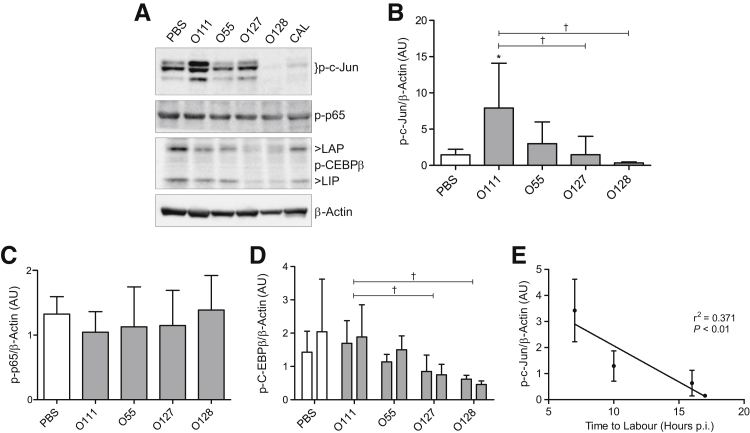
Figure 2.
Activation of myometrial activator protein 1 (AP-1) is strongly induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) O111:B4 and precedes the onset of preterm labor. Examination of myometrial protein lysates collected 6 hours after intrauterine injection of either phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) or LPS (serotypes O111:B4, O55:B5, O127:B8, or O128:B12). Results were analyzed by Western blot analysis for the transcriptionally active phosphorylated forms of AP-1 subunit c-jun (A and B), NF-κB subunit p65 (A and C), and CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein (C/EBPβ) isoforms, liver-enriched activating protein (LAP; first column) and liver-enriched inhibitory protein (LIP; second column) (A and D). Densitometric analysis of immunoreactive protein reveals an increase in p-c-Jun (B), but not p-p65 (C) or C/EBPβ isoforms (D), compared with PBS controls. Linear regression of p-c-Jun levels against time to labor shows a correlation between high levels of myometrial p-c-Jun and rapid onset of preterm labor (E). n = 5 (E). ∗P < 0.05, versus PBS-injected control dams; †P < 0.05, within LPS treatment group (one-way analysis of variance with Tukey's post hoc analysis). AU, arbitrary unit; CAL, calibrator; p.i., postinjection.