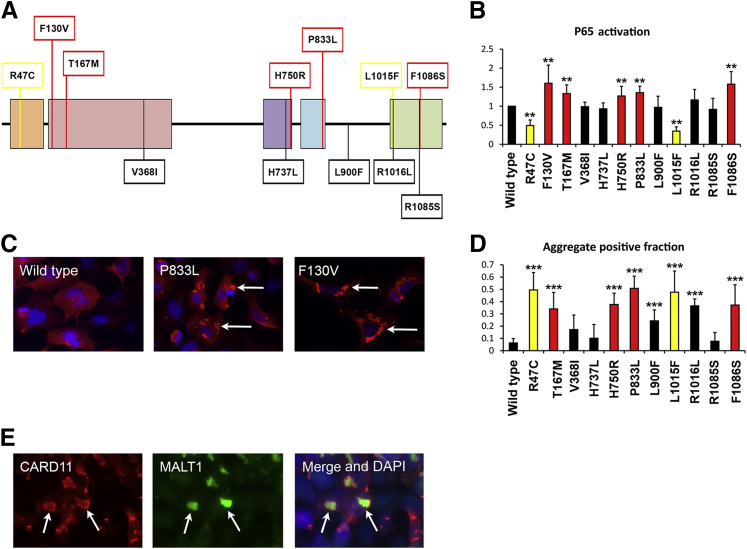
Figure 2.
Multidomain cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC) mutations in CARD11 result in dysregulated NF-κB activity. A: Individual mutations were transfected into HEK 293 cells and P65/NF-κB activity was analyzed using a TransAM enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay 42 hours after transfection. The F130V is a diffuse large B-cell lymphoma–specific CARD11 mutation to increase P65 activation (data not shown). All other mutations are cSCC specific. The initial assessment of CARD11 F130V, R818E, P833L, and R1016K, using individual assays for P50, P52, P65, RELB, and c-REL, identified only P50 and P65 increased activation. All subsequent assays were performed using the P65 TransAM assay. B: The mean of P65 activity relative to wild-type CARD11 for each individual mutation from three to four separate experiments. Red bars indicate CARD11 variants with increased activity compared with CARD11 wild-type, whereas black bars indicate no significant difference. Samples with only background activity comparable with the empty vector control are indicated by yellow bars. C: DDK immunostaining shows the assembly of CARD11 into cytoplasmic aggregates. HEK 293 cells were seeded on coverslips and transfected 24 hours later as described. Forty-two hours after transfection the cells were incubated with an anti-DDK antibody followed by Alexa 594–conjugated secondary antibody (Dako). Arrows indicate representative foci that are reduced in wild-type CARD11-transfected cells. D: A minimum of 200 cells from two separate experiments were scored for the presence of cytoplasmic aggregates and the graph shows the aggregate-positive fraction for each indicated CARD11 transfection. E: Co-localization of DDK-CARD11 and MALT1 in cytoplasmic aggregates (arrows). Immunofluorescence was performed using anti-DDK antibody and anti-MALT1 antibody. ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001, two-sample t-test comparison with wild-type CARD11.