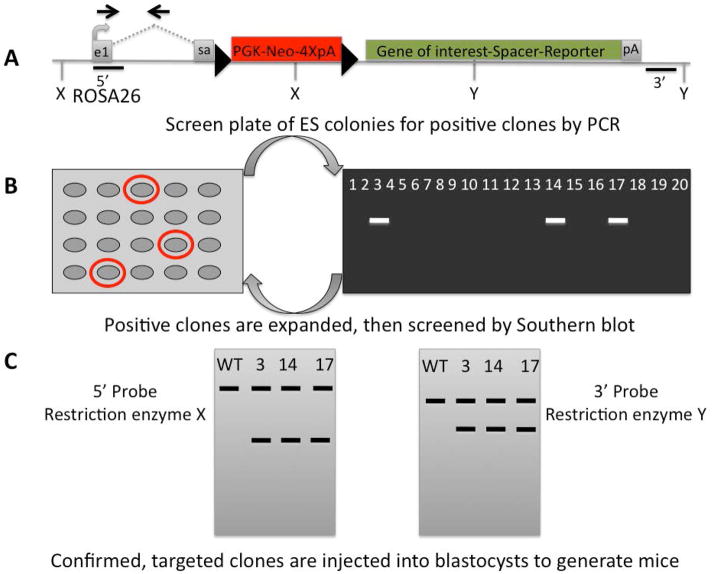
Figure 2.
Targeting the ROSA26 locus for inducible expression of a gene of interest. A) A cassette containing Neomycin as a selectable marker driven by the PGK promoter, followed by 4X poly A (pA) signals is flanked by loxP sequences (black triangles), and placed downstream of a splice acceptor (sa) site in the ROSA26 locus. A gene of interest may be followed by an intervening sequence and a reporter gene such as green fluorescent protein. B) All cells that will grow in neomycin are screened by PCR to determine if they contain the cassette. The Forward (F) primer in the 5′ homology arm also binds to WT ROSA sequence, but the Reverse (R) primer is downstream in unique sequence (does not bind to WT ROSA) (black arrows in A). C) Positive ES cell clones detected by PCR are expanded, and screened by Southern blot using a unique sequence probe from the 5′ end (black line), and from the 3′ end (black line). Restriction enzyme X and Y cut within the gene of interest to produce a smaller product than the wild type. The appropriate size predicts correctly targeted clones. These probes can be used to confirm correctly rearranged alleles after deletion of the floxed STOP cassette with a Cre.