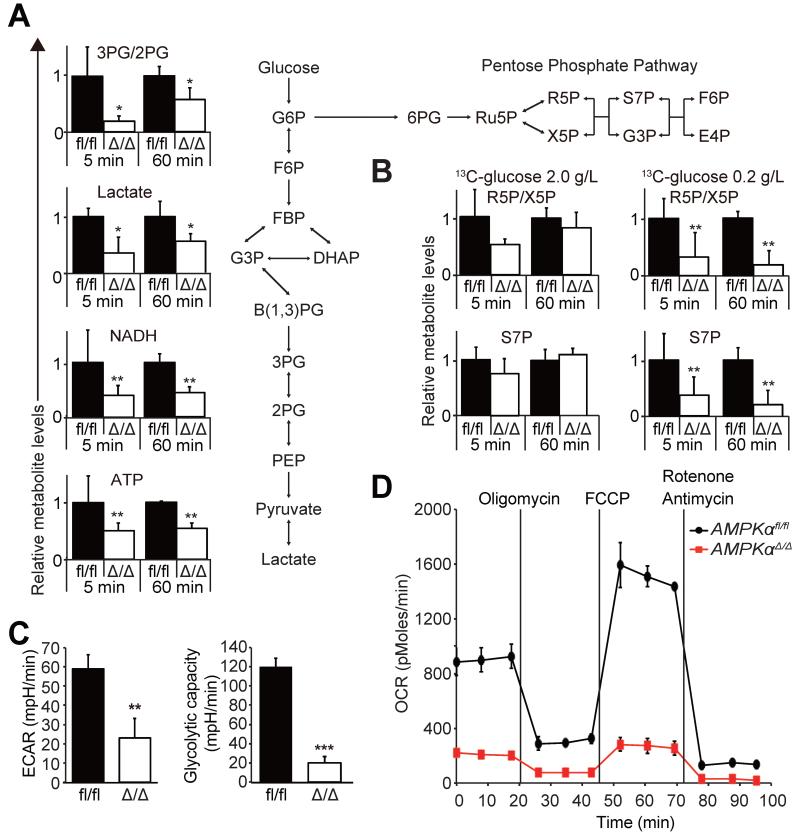
Figure 6. AMPK regulates glucose metabolism.
(A) 13C-glucose flux analysis performed on freshly isolated AMPKαfl/fl and AMPKαΔ/Δ AML cells exposed to 2.0 g/L 13C-glucose for the indicated time revealed significantly reduced 13C incorporation into glycolysis intermediates 3PG/2PG and lactate, in addition to NADH and ATP. The amounts of 13C-labeled metabolites were normalized to the values of AMPKαfl/fl cells (n=3). Schematic of glycolysis and the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) is shown on right. (B) 13C-glucose flux analysis was performed as in (A) with either 2.0 g/L (left panels) or 0.2 g/L glucose (right panels) to access the glucose flux through PPP (n=3). (C) Basal ECAR and ECAR after oligomycin treatment were significantly reduced in freshly isolated AMPKαΔ/Δ AML cells compared to AMPKαfl/fl AML cells (n=3). (D) Extracellular Flux analysis revealed that AMPKαfl/fl AML cells have significantly reduced OCR (n=3). See also Figure S5.