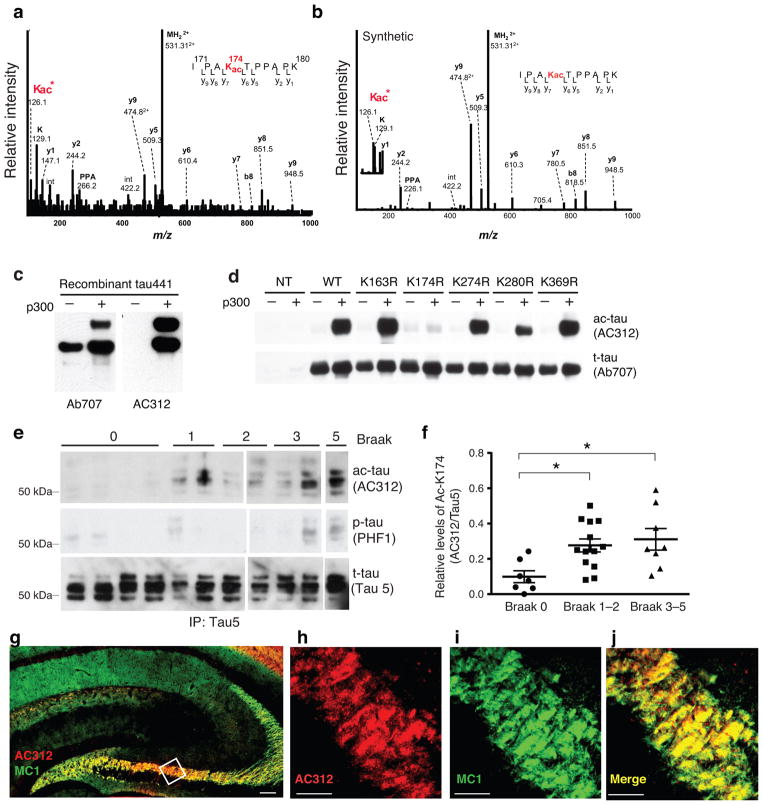
Figure 1. Tau-K174 Is Acetylated at Early Stages of AD.
(a) ESI-MS/MS tandem mass spectra of Lys-acetylated peptide IPAKAcTPPAPK (residues 171–180) with a Protein Pilot confidence score of 99 obtained after trypsin digestion of immunoprecipitated Tau from AD brains. K*: Marker ion at 126.1 for acetyllysine immonium ion identification. (b) ESI-MS/MS tandem mass spectrum of acetyl-lysine containing synthetic peptide IPAKacTPPAPK. The corresponding Protein Pilot confidence score was 99. (c) Immunoblot of recombinant tau in the presence or absence of p300 showing acetyl-tau-specificity of AC312. (d) Immunoblot of lysates from HEK293 cells expressing tau mutants. Mutation of K174R diminished p300-induced immunoreactivity of AC312. (e–f) AC312-positive ac-tau (K174) signal was detected in AD brains (Braak stages 1–5). (e) Immunoblot of Tau5 immunoprecipitates with AC312 and PHF-1 antibodies. (f) Levels of ac-K174 were significantly higher at early and late Braak stages than those at Braak stage 0; n = 7 (Braak 0), n = 13 (Braak 1–2), n = 8 (Braak 3–5). * p < 0.05, one-way ANOVA, Tukey-Kramer post hoc analyses. See Supplementary Table-1 for the patient information. (g–j) AC312 immunoreactivity in the hippocampus of PS19 mice. (g) Merged image of AC312 and MC1 immunostaining at low magnification; scale bar 100 μm. (h–j) High-magnification confocal images showing (h) AC312-positive and (i) MC1-positive tau are highly colocalized (j); scale bar 25 μm. Values are means ± SEM (f). WT, wild-type.