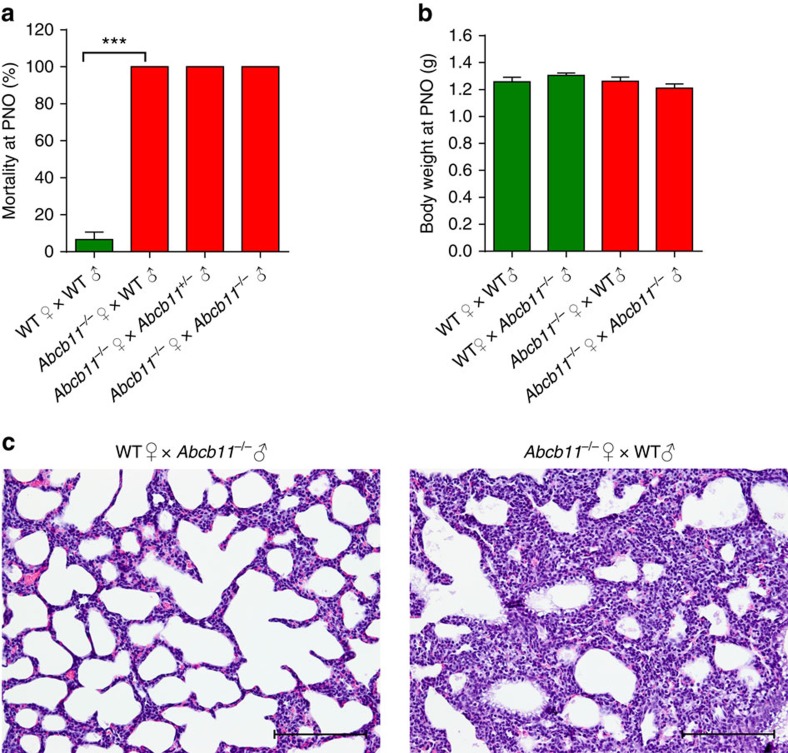
Figure 1. Maternal Abcb11 deficiency produces neonatal lethality.
(a) Abcb11−/− females were interbred with WT (n=2), Abcb11+/− and Abcb11−/− males (n=4). No neonates survived more than 24 h. Green bars indicate WT mother, while red bars indicate an Abcb11−/− mother. (b) BW of neonates at PN0 reveals no significant difference regardless of parentage. WT♀ × WT♂, n=14; WT♀ × Abcb11−/−♂, n=21, Abcb11−/−♀ × WT♂, n=18; Abcb11−/−♀ × Abcb11−/−♂, n=9. (c) Hematoxylin and eosin stain reveals collapsed alveoli from the lungs of neonates carried by Abcb11−/− mothers. All experimental values are presented as mean±s.e.m. The height of the error bar=1 standard error. Statistical analysis was performed using two-tailed Student's t-test, ****P<0.0001. Scale bar, 200 μm.