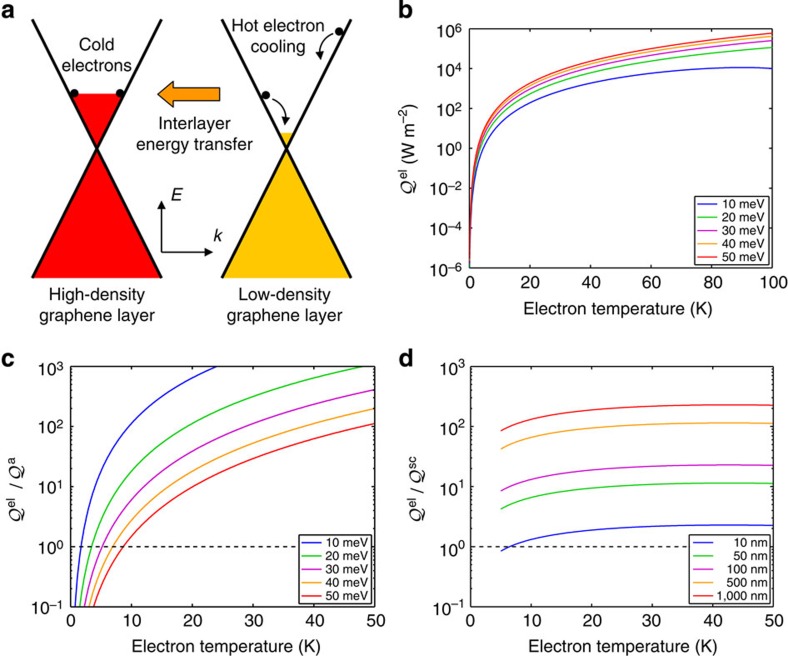
Figure 1. Interlayer Coulombic energy transfer between two graphene layers.
(a) Schematic diagram of interlayer Coulombic energy transfer from a hot LD to a cold HD graphene layer. (b) Cooling power of interlayer Coulombic energy transfer 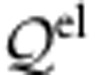 as a function of electron temperature for Fermi level EF,HD=300 meV in the HD graphene layer and various Fermi levels EF,LD in the LD graphene layer. (c) Ratio of the cooling power of interlayer Coulombic energy transfer
as a function of electron temperature for Fermi level EF,HD=300 meV in the HD graphene layer and various Fermi levels EF,LD in the LD graphene layer. (c) Ratio of the cooling power of interlayer Coulombic energy transfer 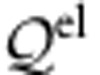 to the cooling power of intralayer acoustic phonon cooling
to the cooling power of intralayer acoustic phonon cooling 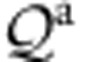 as a function of electron temperature for EF,HD=300 meV, and various values of EF,LD showing that interlayer Coulombic energy transfer can dominate intralayer acoustic phonon cooling in the LD graphene layer. (d) Ratio of the cooling power of interlayer Coulombic energy transfer
as a function of electron temperature for EF,HD=300 meV, and various values of EF,LD showing that interlayer Coulombic energy transfer can dominate intralayer acoustic phonon cooling in the LD graphene layer. (d) Ratio of the cooling power of interlayer Coulombic energy transfer 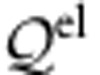 to the cooling power of intralayer disorder-assisted electron–phonon (supercollision) cooling
to the cooling power of intralayer disorder-assisted electron–phonon (supercollision) cooling 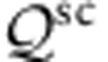 as a function of electron temperature for EF,HD=300 meV, EF,LD=10 meV (typical for C-face MEG on SiC) and various values of the disorder mean free path in the LD graphene layer showing that interlayer Coulombic energy transfer can dominate intralayer disorder-assisted electron–phonon (supercollision) cooling in the LD graphene layer.
as a function of electron temperature for EF,HD=300 meV, EF,LD=10 meV (typical for C-face MEG on SiC) and various values of the disorder mean free path in the LD graphene layer showing that interlayer Coulombic energy transfer can dominate intralayer disorder-assisted electron–phonon (supercollision) cooling in the LD graphene layer.