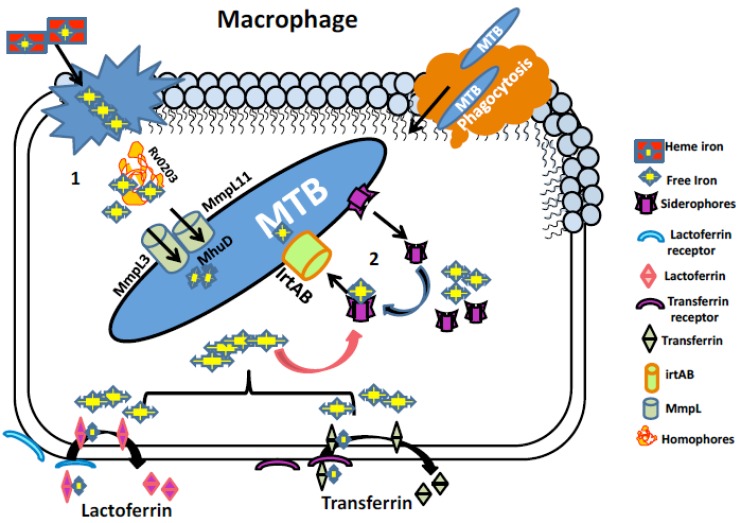
Fig. (1).
Iron acquisition mechanisms in MTB. (1) Iron uptake pathway utilizing heme source. Free heme from senescent RBCs engulfed by macrophages is bound to homophore Rv0203 and brings them to membrane proteins Mmpl3 and Mmpl11. These proteins transport heme to MTB cytoplasm where heme degrading protein MhuD degrades heme to release free iron. (2) Iron acquisition utilizing non-heme iron sources mediated by siderophores (Carboxymycobactin/ Mycobactin). Iron associated with host iron proteins i.e. transferrin and lactoferrin enters macrophage through their respective receptors where the siderophores synthesized by MTB chelates free iron and lactoferrin and transferrin are recycled. Siderophore bound iron is then transported to MTB cytoplasm via irtAB, an ABC family transporter protein.