FIG 1.
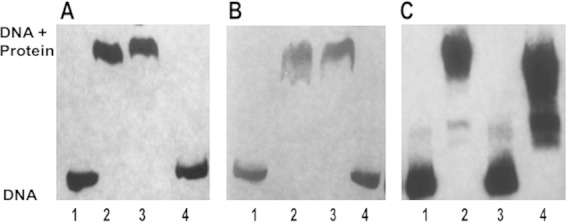
Binding of TetR21 to promoter DNA of tet38, norB, and tetR21 and binding of MgrA to tetR21 DNA. (A) Gel mobility shift analyses of the interactions of the purified TetR21 protein with the biotinylated tet38 promoter. Protein (200 ng, 7.2 pmol) and DNA (4 ng, 20 fmol) were in contact for 30 min at room temperature, followed by electrophoresis through a 5% acrylamide gel. Competing unlabeled herring sperm DNA (nonspecific, 100-fold excess) and unlabeled tet38 promoter (specific, 100-fold excess) were used to determine the specificity of the promoter binding assay. Lane 1, tet38 promoter; lane 2, tet38 + TetR21; lane 3, tet38 + TetR21 + 100-fold herring DNA; lane 4, tet38 +TetR21 + 100-fold unlabeled tet38. (B) Gel mobility shift analyses of the interactions of the purified TetR21 protein with the biotinylated norB promoter. Competing unlabeled herring sperm DNA (nonspecific, 100-fold excess) and unlabeled norB promoter (specific, 100-fold excess) were used to determine the specificity of the norB promoter binding. Lane 1, norB promoter; lane 2, norB + TetR21; lane 3, norB + TetR21 + 100-fold herring DNA; lane 4, norB + TetR21 + 100-fold unlabeled norB. (C) Gel mobility shift analyses of the interactions of the purified TetR21 and MgrA protein with the biotinylated tetR21 promoter. The same procedure was carried out as described above. Lane 1, tetR21 promoter; lane 2, tetR21 + TetR21; lane 3, tetR21 promoter; lane 4, tetR21 + MgrA.
