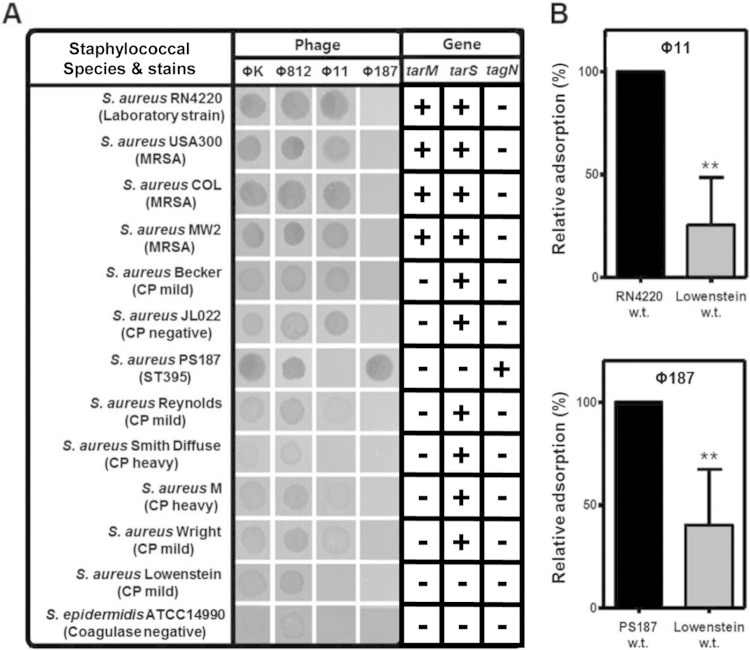
FIG 4.
Correlation between phage susceptibility and the presence of WTA glycosyltransferases. The phage susceptibilities of various S. aureus wild-type strains and S. epidermidis strain ATCC 14990 were determined. Lysates were spotted onto bacterial lawns, and macroplaque formation was analyzed after overnight incubation. The presence (+) or absence (−) of the WTA glycosyltransferase-encoding genes tarM, tarS, and tagN in the corresponding genome is indicated. The tarM, tarS, and tarN genes were amplified from genomic DNA by using the corresponding primers listed in Table S1 in the supplemental material. (B) Rates of phage Φ11 or Φ187 absorption by the S. aureus Lowenstein wild-type (w.t.) strain. The results are representative of those from three independent experiments. The rate of phage adsorption relative to the rate of adsorption of phage Φ11 or Φ187 by strain RN4220 or PS187, which was set equal to 100%, is shown, and results are given as means ± SDs (n = 3). Statistically significant differences compared with the results for the strains that absorbed the phages were determined by the unpaired two-tailed Student's t test. **, P < 0.001 to 0.01.