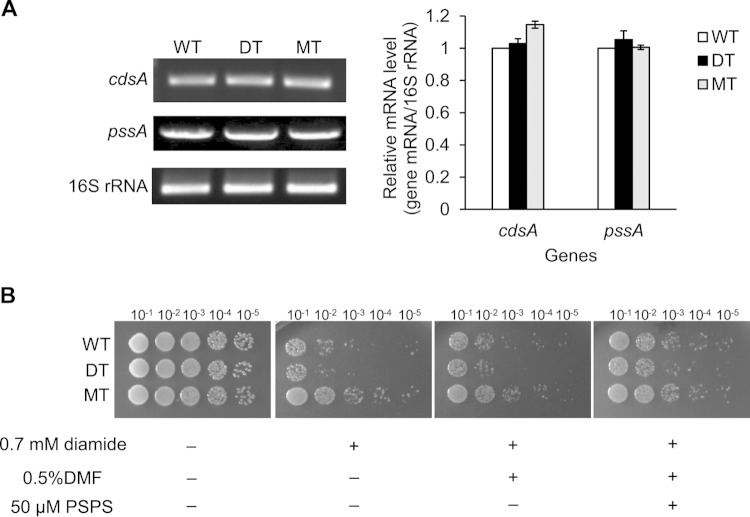
FIG 4.
Effects of the expression of MdsABC on bacterial biosynthesis of phosphatidylserine and resistance to diamide. (A) Expression levels of the cdsA and pssA genes, coding for CDP-diacylglycerol synthase and CDP-diacylglycerol:serine O-phosphatidyltransferase, respectively, which determine the rate of phosphatidylserine biosynthesis in S. Typhimurium. The 16S rRNA control was measured by semiquantitative RT-PCR with total RNA extracts obtained from exponentially growing cell cultures of the WT, DT, and MT strains in the presence of 0.1% arabinose. Band intensity was quantified by densitometry and normalized based on the level of 16S rRNA. Results from three independent culture experiments are reported as the mean ± SD. (B) Spot dilution assays of S. Typhimurium strains showed an increase in diamide resistance with the addition of 50 μM 1-palmitoyl-2-stearoyl-phosphatidylserine (PSPS). Dimethylformamide (DMF) (final concentration, 0.5%) was used as a solvent control.