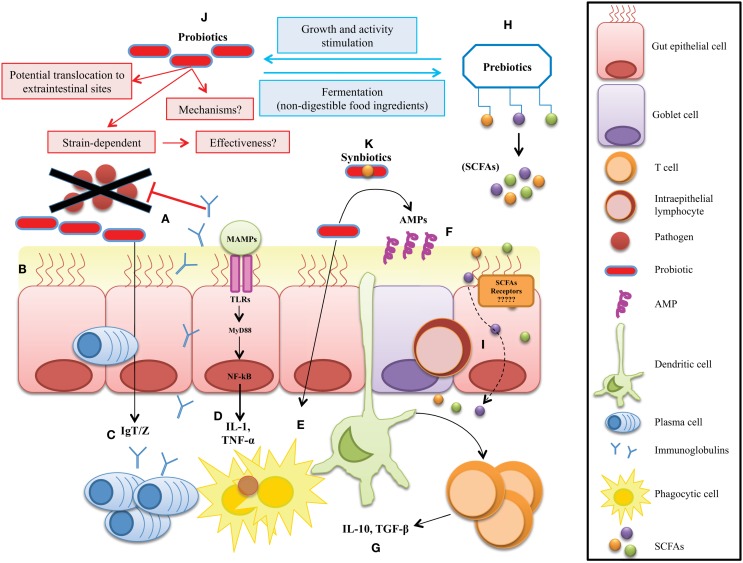
Figure 1.
Potential microbial strategies to improve gut mucosal immunity in fish. The therapeutic approach mechanisms include: (A) competitive exclusion for binding sites and translocation, (B) enhanced barrier function by reversing the increased intestinal permeability, (C) enhanced mucosal immunoglobulin IgT/Z response to enteral antigens, (D) reduction of secretion of inflammatory mediators, (E) stimulation of innate immune functions, (F) stimulate the release of antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) at the mucosal layer, and (G) enhanced availability of anti-inflammatory mediators by regulatory immune cells. (H) Production of metabolic health-enhancers like SCFAs by non-digestible prebiotics, (I) diffusion of SCFAs through the enterocytes to improve mucosa barrier functions. (J) Probiotics have been suggested to confer several health benefits on the host. However, their mechanisms of action are not well understood. (K) Synbiotics are a mix of pre- and probiotics, thus their mode of action are much more difficult to define.