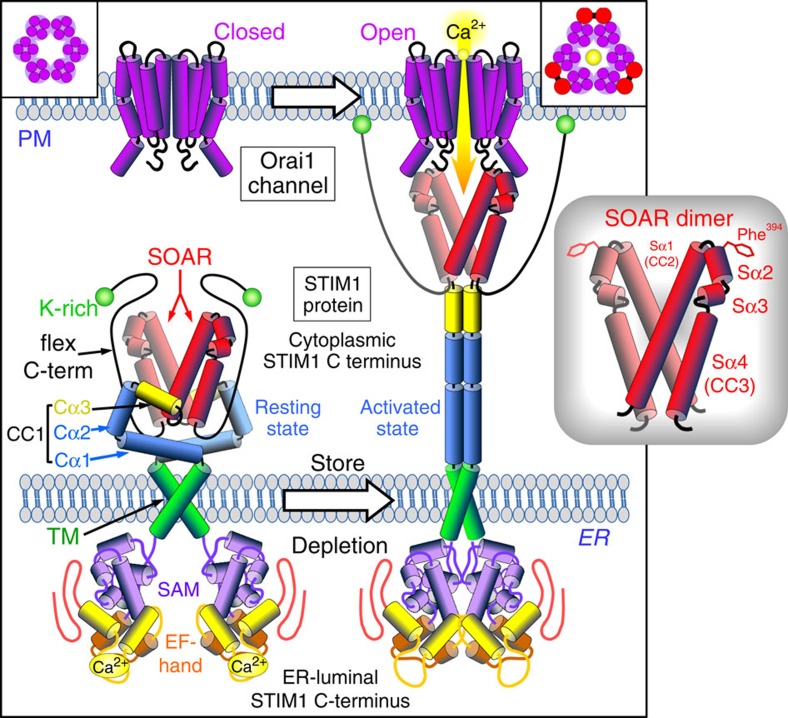
Figure 1. Molecular model of the activation and coupling of STIM1 to activate the Orai1 channel.
The dimeric, single transmembrane-spanning STIM1 ER protein senses ER luminal Ca2+ change through its N-terminal complex of EF hands and sterile-α motif (SAM). The STIM1 cytoplasmic C terminus is a largely helical complex including the CC1 region, the STIM-Orai-activating region (SOAR), and a flexible C terminus ending with a K-rich region. In the STIM1-resting state, the EF hand/SAM domains are separated, and the SOAR region is occluded within a folded complex of SOAR, CC1 and the flexible C terminus. On luminal Ca2+ store depletion, Ca2+ dissociation from the EF hand/SAM domains allows the N termini to associate forcing a conformational change in the STIM1 C terminus mediated through rearrangement of the TM domains. The STIM1 C terminus undergoes unfolding and elongation through dissociation between the CC1 and SOAR regions. The extended, unfolded C terminus allows the K-rich C termini of STIM1 to bind to the PM, and also exposes SOAR in this extended configuration allowing it to associate with PM Orai1 channels within closely membrane-associated ER–PM junctions. Orai1 is a four transmembrane-spanning PM protein, forming hexameric Ca2+ channels (box, left). Orai1 channels can be tethered within ER–PM junctions by the extended, exposed SOAR unit of activated STIM1. SOAR binding to Orai1 induces gating of the channel to allow Ca2+ entry. On the basis of recent information, the model depicts interaction between the SOAR dimer and two adjacent Orai1 subunits of the channel hexamer (box, top right). A more detailed diagram of the molecular organization of the SOAR dimer (inset, right) is from the crystal structure10. Each monomer has four α-helices, interacting together through hydrophobic and hydrogen bonding at three interfaces. The two larger helices, Sα1 and Sα4 (also known as CC2 and CC3, respectively), flank two smaller helices (Sα2 and Sα3). The apical Sα2 helix includes an exposed residue, phenylalanine-394, shown to be critical to the binding and gating of Orai1 channels by STIM1 (ref. 20).