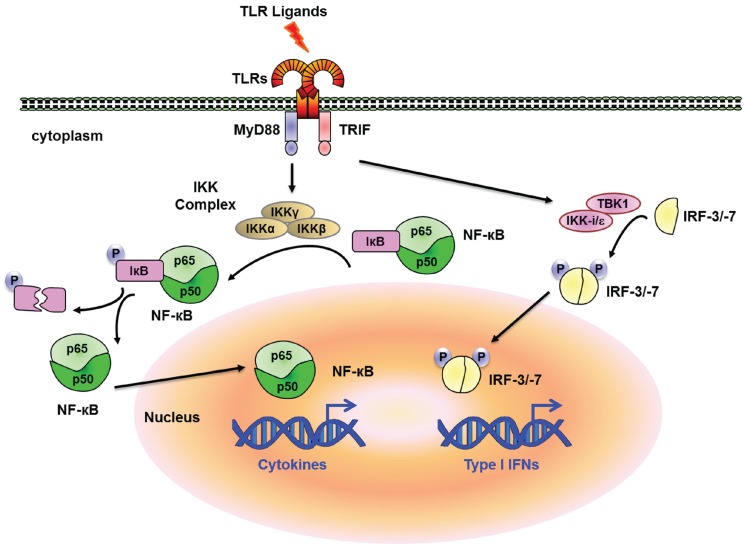
Figure 1.
TLR Signaling and NF-κB activation. Stimulation of TLRs trigger the association of The Toll/interleukin-1 (IL-1)-receptor (TIR)-domain-containing adaptor molecule MyD88 which mediates the TLR-signaling pathway leading to the activation of the IKK complex, which consists of IKK-α, IKK-β and IKK-ɣ (also known as IKK1, IKK2 and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) essential modulator, NEMO, respectively). This pathway is used by TLR1, TLR2, TLR4, TLR5, TLR6, TLR7 and TLR9 and degradation of the phosphorylated IκB by the ubiquitin proteasome system allows the translocation of NF-κB to the nucleus where it activates the expression of cytokine genes (Il6, Tnf, etc.). Another TIR-domain-containing adaptor, TRIF, is essential for the MyD88-independent pathway. The non-typical IKKs IKK-ε and TBK1 mediate phosphorylation of IRF3/7 downstream of TRIF. This phosphorylated IRF3/7 translocates into the nucleus to induce expression of type I IFN and IFN inducible genes (Ifnb, Cxcl10, etc.).