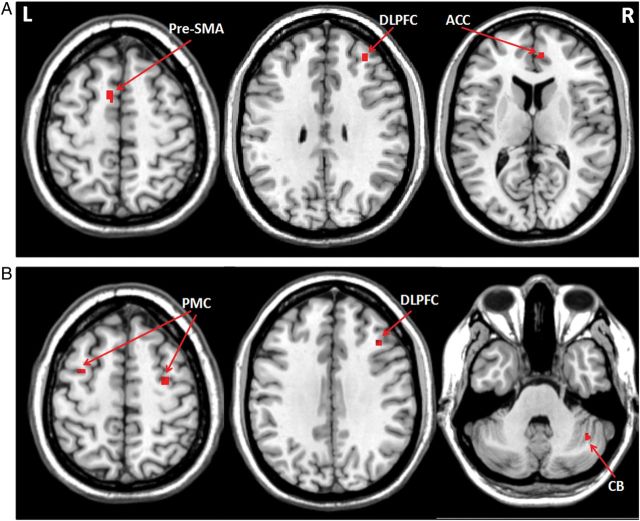
Figure 5.
Brain regions more activated when attending to an automatic movement. Brain regions more activated in attention than in automatic stage in controls (A), and Parkinson's disease patients (B) when performing the visuomotor association task (post hoc t-test, P < 0.05, FWE corrected). Attention to the automatic task increased activations in the right DLPFC (MNI coordinates 34, 43, 32), right ACC (6, 46, 11), and left pre-SMA (−10, 6, 55) in controls, and enhanced activity in the right DLPFC (42, 25, 34), bilateral PMC (−32, 2, 52, and 32, −6, 55), and right cerebellum (40, −55, −35) in patients compared with the automatic stage (Table 4). L, left; R, right; ACC, anterior cingulate cortex; CB, cerebellum; DLPFC, dorsolateral prefrontal cortex; PMC, premotor cortex; pre-SMA, rostral supplementary motor area.