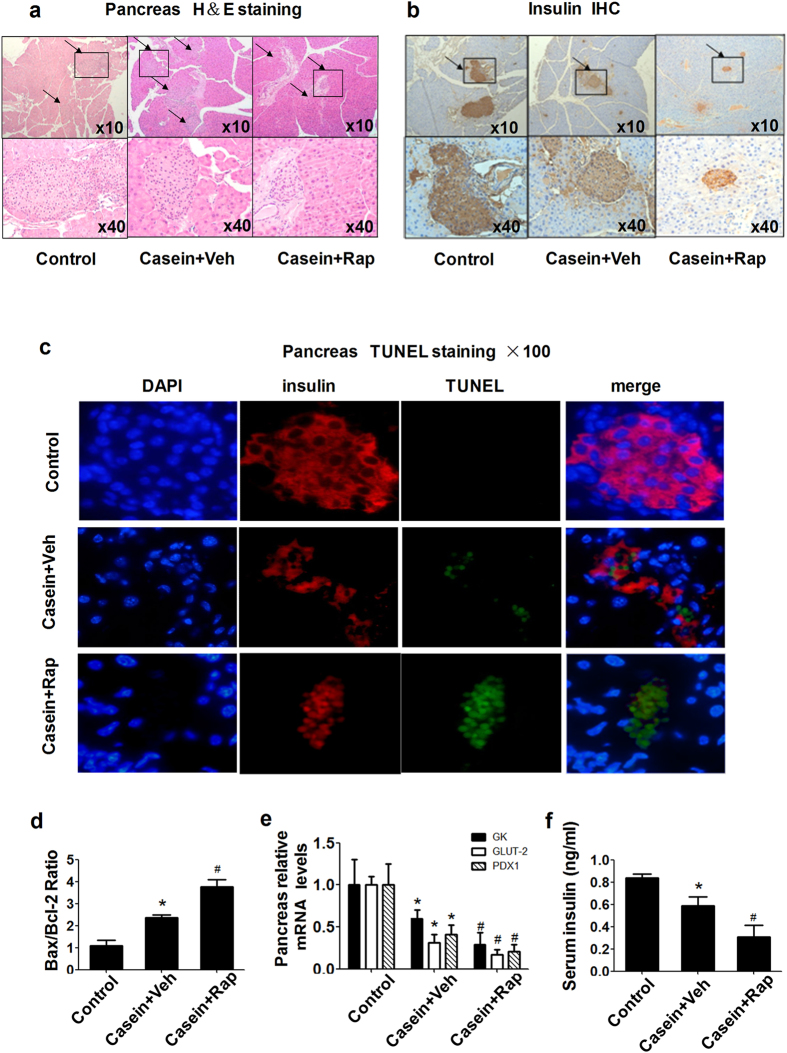
Figure 7. Rapamycin induced pancreatic β-cell dysfunction and apoptosis in vivo.
(a) Hematoxylin–eosin staining in the pancreas. (b) Insulin immunohistochemistry. Magnification, 10× (top panels); 40× (bottom panels). (c) Apoptosis in situ. Apoptosis of insulin-expressing cells on islet sections was determined by the TUNEL assay. Representative examples of pancreatic islets stained by immunofluorescence for insulin (red), marker of cell apoptosis TUNEL (green), and nuclear stain DAPI (blue) imaged at 100× in casein plus vehicle (upper) and casein plus rapamycin (lower). (d) Effects of rapamycin on the mRNA expression of Bax/Bcl2 in the pancreas of C57BL/6J mice. (e) Effects of rapamycin on β-cell gene expression. The expression of GK, GLUT2 and PDX-1 in islets was determined by real-time quantitative RT-PCR using β-actin as an internal standard. (f) Serum insulin concentrations in C57BL/6J mice were analyzed using a mouse-specific insulin ELISA kit. The results represent the mean ± SD (n = 6). *P < 0.05 versus control, #P < 0.05 versus casein plus vehicle.