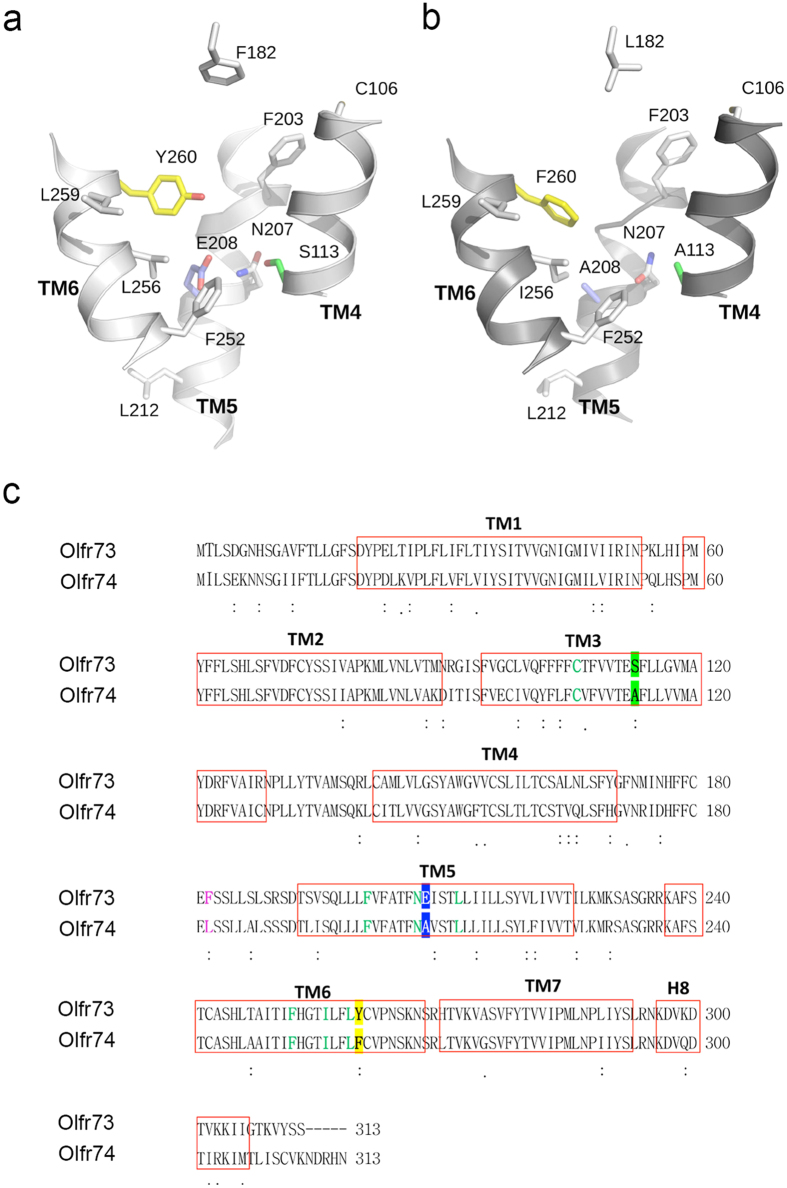
Figure 1. Predicted 3D models of Olfr73 and Olfr74 odorant binding pockets.
(a) Experimentally confirmed amino acid residues functionally relevant for odorant detection in Olfr73: C106 (TM3), S113 (TM3), F182 external loop (EL2), F203 (TM5), N207 (TM5), E208 (TM5), L212 (TM5), F252 (TM6), I256 (TM6), L259 (TM6), Y260 (TM6) are compared with homologous amino acid positions in Olfr74 (b). Different amino acids in positions 113, 208 and 260 of both paralogs are indicated with green, blue and yellow colors, respectively. (c) Sequence alignment between Olfr73 and Olfr74. Residues functionally important for odorant detection in Olfr73 and identical in Olfr74 are shown in mint color, those that differ are shown in green, blue and yellow, respectively. Different amino acids in position 182 (EL2) are shown in violet. The putative TMs are boxed in red.